INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE (1:2:1)
Sometimes two genes of allelomorphic pair do not show dominant-recessive relationship, but when present simultaneously (or come together), they show intermediate condition or blend together, which is called incomplete dominance. It is due to the fact that the dominant character or gene is not in a position to completely suppress the recessive one. With the result, the heterozygote has a different phenotype (as well as different genotype) from homozygous for either allele.
- First case of incomplete dominance was reported in Mirabilis jalapa (4 o'clock plant) by Carl Correns (1903).
Incomplete dominance is found in both plants and animals. Good examples are seen in Mirabilis jalapa, Antirrhinum majus, (snapdragon) and Andalusian fowl.
Example :- 1
In Mirabilis jalapa (4 o'clock plant) and Antirrhinum majus (Snapdragon or Dog flower) there are two types of flower colour in pure state, red and white.
A cross between a plant pure for red flowers and a plant pure for white flowers yield hybrid plants with pink flowers in F1 generation. Neither red nor white is completely dominant, so that both colour appear in the hybrids as a blend which is pink. This is obviously a contradiction of Mendel's assumption that no blending of characters takes place. When two of the hybrid plants with pink flowers are crossed, the F2 generation includes plants with red, pink and white flowers in the usual Mendelian ratio of 1 : 2 : 1.
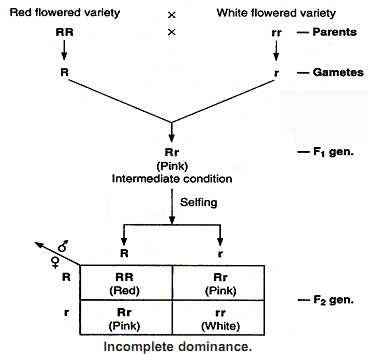
Incomplete dominance.
This cross shows :-
(i) Incomplete dominance.
(ii) The genes for red and white colour do not actually mix in the F pink hybrids as both the pure characters (red and white) reappear in the F1 plants.
(iii) There is no specific gene for pink flowers.
(iv) Quantitative effect of genes. The homozygous plants rr are unable to produce the flower pigment. The heterozygous plants Rr can produce only half the amount of flower pigment that is produced by the homozygous plant RR. In the F2 generation of the above cross :-
(i) The genotypic ratio is the same as Mendelian ratio, being 1 : 2 : 1 (1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr).
(ii) The phenotypic ratio differs from the Mendelian ratio, also being 1 : 2 : 1 (red : pink : white) instead of 3 : 1 (red : white).
(iii) Half of the F2 generation show F1 phenotype instead of 3/4.
The phenotypic F2 ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 is characteristics of incomplete dominance.
Example :- 2
Incomplete dominance is also found in Andalusian fowl. The Andalusian fowl is found in three colours : Black, white and blue. Pure forms are black (BB) and white (bb). If these two forms are crossed, F1 individuals appear blue (Bb) coloured. The blue hybrids on crossing with each other (Bb, Bb) give rise to one black (BB), two blue (Bb) and one white (bb) in 1 : 2 : 1 ratio. The blue appearance of the hybrids is due to very fine alternating white and black strips on the feathers.