Illustration of Marginal profit
To illustrate the computations, suppose that the marginal profit or XE in our model is changed from 3 to 3 + δ1, where δ represents either positive or negative change. This means that the objective function reads as: Z = (3 + δ1) XE + 2XI.
If we use this information in the starting tableau and carry out the same arithmetic operations used to produce the optimum tableau, the optimum Z equation will appear as:
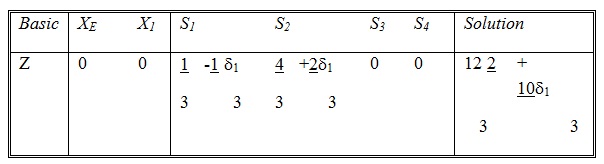
This equation is the same as the optimum Z equation before the change δ1 is effected, modified by terms of δ1. The coefficients of δ1 are essentially those in the XE equation of the optimum tableau, which are
Pivot Element
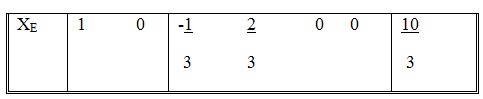
We choose the XE equation because XE is the variable whose objective coefficient is being changed by δ1.
The change δ1 will not affect the optimality of the problem as long as all the Z equation coefficients of the non-basic variables remain non-negative (maximization) that is:
1/3 - δ1/3 ≥0
4/3 + 2δ1/3 ≥ 0
First Relationship shows that δ1 ≥ 1 and the relation second yields δ1 ≥ -2. Both relations limit δ1 by -2 ≤ δ1 ≤ 1. This means that the coefficient of XE can be as small as 3 + (-2) = 1 or as large as 3 + 1 = 4 without causing any change in the optimal values of the variables. The optimal value of Z, however, will change according to the expression 12 2/3 + 10/3 δ1 where -2 ≤ δ ≤ 1.
The foregoing discussion assumed that the variable whose coefficient is being changed has an equation in the constraints. This is true only if the variable is basic (such as XE and XI above). If it is non-basic, it will not appear in the basic column.
The treatment of non-basic variable is straight forward. Any change in the objective coefficient of a non-basic variable will affect only that coefficient in the optimal tableau. To illustrate this point, consider changing the coefficient of SI (the first slack variable) from 0 to 0 + δ3. If you carry out the arithmetic operations leading to the optimum tableau, the resulting Z equation becomes:
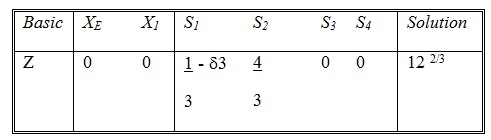
It shows that the only change occurs in the coefficient of SI, where it is decreased by δ3. As a general rule, then, all we have to do in the case of a non-basic variable is to decrease the Z coefficient of the non-basic variable by the amount by which the original coefficient of the variable is increased.