Illustration of a Clipping window ABCD is placed as follows:
A (100, 10), B (160, 10, C (160, 40), D (100, 40)
By using Sutherland-Cohen clipping algorithm determine the visible portion of the line segments i.e. EF, GH and P1P2. E (50, 0), F (70, 80), G (120, 20), H (140, 80), P1 (120, 5), P2(180, 30).
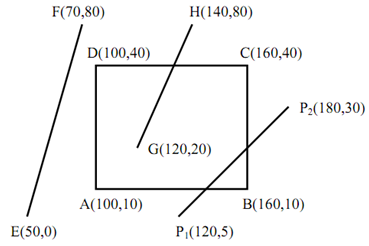
Figure: Example of Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping
At first identifying the line P1P2
INPUT: P1(120, 5), P2(180, 30)
xL = 100, xR = 160, yB = 10, yT = 40
x1 > xL then bit 1 of code -P1 = 0 C1 left = 0
x1 < xR then bit 2 of code -P1 = 0 C1 right = 0
y1 < yB then bit 3 of code -P1 = 1 C1 bottom = 1
y1 < yT then bit 4 of code -P1 = 0 C1 top = 0
code -P1 = 0100,
x2 > xL then bit 1 of code -P1 = 0 C2 left = 0
x2 > xR then bit 2 of code -P1 = 1 C2 right = 1
y2 > y B then bit 3 of code -P1 = 0 C2 bottom = 0
y2 < yT then bit 4 of code -P1 = 0 C2 top = 0
code -P2 = 0010.
Both code -P1 <> 0 and code -P2 <> 0
then P1P2 not totally visible
code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0000
therefore (code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0)
then line is not fully invisible.
As code -P <> 0
for i = 1
{
C1 left (= 0) <> 1 then nothing is done. i = i + 1 = 2
}
code -P1 <> 0 and code -P2 <> 0
then P1P2 not totally visible.
code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0000
therefore (code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0)
then line is not fully invisible.
for i = 2
{
C1 right (= 0) <> 1 then nothing is to be done. i = i + 1 = 2 + 1 = 3
}
code -P1 <> 0 and code -P2 <> 0 then P1P2 not totally visible.
code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0000
therefore, (code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0)
then the line is not fully invisible.
for i = 3
{
C1 bottom = 1 then find intersection of P1P2 with bottom edge yB = 10
xB = (180-120)(10-5)/(30-5) + 120
=132
then P1 = (132,10)
x1 > xL then bit 1 of code -P1 = 0 C1 left = 0
x1 < xR then bit 2 of code -P1 = 0 C1 right = 0
y1 = yB then bit 3 of code -P1 = 0 C1 bottom = 0
y1 < yT then bit 4 of code -P1 = 0 C1 top = 0
code -P1 = 0000
i = i + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
}
code -P1 <> 0 but code -P2 <> 0
then P1P2 not totally visible.
code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0000
therefore, (code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0)
then line is not fully invisible.
As code -P1 = 0
Swap P1 and P2 along with the respective flags
P1 = (180, 30) P2 = (132, 10) code -P1 = 0010 code -P2 = 0000
C1 left = 0 C2 left = 0
C1 right = 1 C2 right = 0
C1 bottom = 0 C2 bottom = 0
C1 top = 0 C2 top = 0
Reset i = 1
for i = 1
{
C1 left (= 0) <> 1 then nothing is to be done. i = i + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
}
code -P1 <> 0, and code -P2 <> 0
then P1P2 is not totally visible.
code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0000
therefore, (code -P1 AND code -P2 = 0)
then line is not fully invisible.
for i = 2
{
C1 right = 1 then find out intersection of P1P2 with right edge xR = 160
yR = (30 - 5)(160 - 120)/(180 - 120) + 5
= 21.667
= 22 then P1 = (160, 22)
x1 > xL then bit 1 of code -P1 = 0 C1 left = 0
x1 = xR then bit 2 of code -P1 = 0 C1 right = 0
y1 > yB then bit 3 of code -P1 = 0 C1 bottom = 0
y1 < yT then bit 4 of code -P1 = 0 C1 top = 0
code -P1 = 0000, i = i + 1 = 2 + 1 = 3
}
As both code -P1 = 0 and code -P2 = 0 then the line segment P1P2 is completely visible.
Consequently, the visible portion of input line P1P2 is P'1P'2 where, P1 = (160, 22) and
P2 = (132, 10).
For the line EF
1) The endpoint codes are allocated code:
code - E → 0101
code - F → 1001
2) Flags are allocated for the two endpoints:
Eleft = 1 (as x coordinate of E is less than xL)
Eright = 0, Etop = 0 and Ebottom = 1
As the same,
Fleft = 1, Fright = 0, Ftop = 1 and Fbottom = 0
3) Because codes of E and F are both not equivalent to zero the line is not wholly visible.
4) Logical intersection of codes of E and F is not equivalent to zero. Consequently, we may avoid EF line and declare it as wholly invisible.
Identifying the line GH:
a) The endpoint codes are allocated:
code - G → 0000 and
code - H → 1000
b) Flags are allocated for the two endpoints:
Gleft = 0, Gright = 0, Gtop = 0 and Gbottom = 0.
As the same,
Hleft = 0, Hright = 0, Htop = 1 and Hbottom = 0.
c) Because, codes of G and H are both not equivalent to zero according to the line is not totally visible.
d) Logical intersection of codes of G and H is equivalent to zero consequently we cannot specify it as completely invisible.
f) Because, code - G = 0, Swap G and H with their flags and set i = 1
Implying Gleft = 0, Gright = 0, Gtop = 1 and Gbottom = 0.
Hleft = 0, Hright = 0, Htop = 0 and Hbottom = 0.
The same as G → 1000 and H → 0000
6) Because, code - G <> 0 then
for i = 1,
{since Gleft = 0
i = i + 1 = 2
go to 3
}
The conditions 3 and 4 don't hold and so we can't declare line GH as completely visible or invisible.
for i = 2, {since Gright = 0
i = i + 1 = 3
go to 3
}
The conditions 3 and 4 don't hold and so we can't declare line GH as completely visible or invisible.
for i = 3, {since Gbottom = 0
i = i + 1 = 4
go to 3
}
The conditions 3 and 4 don't hold and so we can't declare line GH as completely visible or invisible.
for i = 4, {since Gtop = 1
Intersection along with top edge, as P(x, y) is found as given below:
Any of line passing via the points G, H and a point P(x, y) is given via y - 20 = {(180 - 20) /(140 - 120)}(x - 120) or, y - 20 = 3x - 360 or, y - 30 = -340
Because, the y coordinate of every point on line CD is 40, consequently we put y = 40 for the point of intersection P(x, y) of line GH along with edge CD.
40 - 3x = -340 or, - 3x = - 380
Or else x = 380/3 = 126.66 ≈ 127
Consequently, the point of intersection is P (127, 40). We allocate code to it.
Because, the point lays on edge of the rectangle hence the code allocated to it is 0000. Here, we allocate G = (127, 40); i = 4 + 1 = 5. State 3 and 4 are again checked. Because, codes G and H are both are equivalent to 0, hence, the line among H(120, 20) and G(127, 40) is wholly visible.