Q. Explain Specific Heat and caluclate amount of heat transferred?
Ans.
The amount of heat transferred to a substance depends on three things:
a) amount of the substance
b) the change in temperature
c) the ability of the substance to absorb heat.
As any of the three things above increases, then the energy transferred increases too.
The ability of a substance to absorb heat is described by a certain number known as the specific heat of the substance. The specific heat, represented by the letter c,( in cal/g oC) of a material is a number which gives us an idea of how much heat is needed to raise the temperature of one gram of the material one Celsius degree. The SI units of specific heat are J/g oC.
This is a property of materials which explains why some foods remain hotter longer than others. You are more likely to burn your tongue on the filling of a hot apple pie than the crust.
This tells you experimentally that the apple pie filling has a greater specific heat (it takes more heat to bring one gram of it to a given temperature or you must remove more heat to drop the temperature of one gram) than the crust.
Water has one of highest specific heats at 1 cal/g oC. One gram of water is able to absorb and hold more heat than other liquids. This is why before the advent of electric blankets and heating pads, the use of hot water bottles was common. It also means that when water is cold, it can absorb more heat as it warms up. This is why we use ice in our coolers to keep our food and drinks cold, and cold water circulating in tubing is often used to cool many things including an astronaut in his/her space suit. This is also the main reason why the outdoor temperature near bodies of water is moderated. It tends to be cooler in summer and warmer in winter near the beach.
Using the specific heat of a substance you can calculate the heat lost or gained depending on the temperature change. As we said before, the amount of heat transferred to a substance depends on the mass, the temperature change and the specific heat.
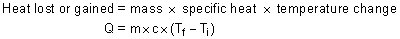
For some reason, we represent heat with the letter Q. Temperature change is the final temperature minus the original temperature. If Q turns out to be negative then there was a heat loss. If it is positive then it is a heat gain.