Q. Illustrate Core Losses in magnetic core material?
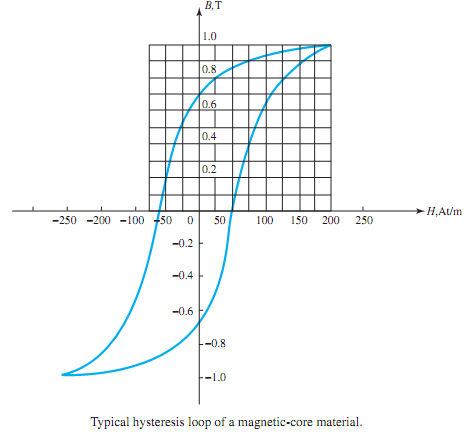
Iron-core losses are usually divided into two components: hysteresis loss and eddy-current loss. The former is proportional to the area enclosed by the hysteresis loop, shown in Figure,
which is a characteristic of a magnetic core material. The area of the loop represents the heat - energy loss during one cycle in a unit cube of the corematerial. The hysteresis loss per cyclePh cycle in a core of volume V, possessing a uniform flux density B throughout its volume, is given by
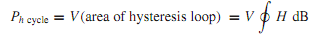
The hysteresis loss per second is approximated empirically by
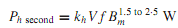
where kh is a proportionality constant dependent on the characteristics of iron, f is the frequency of excitation in hertz, and Bm is the maximum value of the core flux density. This loss component of the core loss can be reduced by choosing a core of electrical steel that has a narrowhysteresis loop. Square-loopmagneticmaterials (such as ferrites and permalloy) that have a nearly rectangular hysteresis loop are used in switching circuits, as storage elements in computers, and in special types of transformers in electronic circuits.
Another feature of an ac-operated magnetic system is the eddy-current loss, which is the loss due to the eddy currents induced in the core material. The eddy-current loss is empirically approximated as
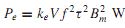
where ke is a constant dependent on the characteristics of iron, V is the volume of iron, f is the frequency, τ is the lamination thickness (usually a stack of thin laminations makes up the core), and Bm is the maximum core flux density. By choosing very thin laminations (making τ smaller), the eddy-current loss can be reduced.
The laminations (or thin sheets), insulated from each other by a thin coat of varnish, are oriented parallel to the direction of flux, as shown in Figure. Laminating a core generally results in an increase in the overall volume. The ratio of the volume actually occupied by the
magnetic material to the total (gross) volume of the core is known as the stacking factor. The thinner the lamination thickness, the lower the stacking factor. This factor usually ranges between 0.5 and 0.95.