IF ... ELSE STATEMENT:
We are familiar with an easy form of the IF statement. The common form of the IF statement is as shown below:
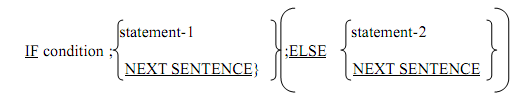
Each of the statement-1 and statement-2 shows one or more COBOL statement. Whenever more than one statement is specified then they should be divided by one or more spaces or by an optional semicolon (;) or by comma (,). During execution, when the condition is found to be true, the statements presented by statement-1 are executed. On the other hand, when the condition is found to be false, the statements presented by statement-2 are executed. For ease of the reference, we shall call the statements represented by statement-1 and statement-2 as then part or else part respectively.
It may be noted that either the then Part or else part is executed depending on the value of the specified condition. Afterward, the control implicitly goes to the statement that instantly follows the IF sentence.
Generally, an If statement must be terminated by the period (.) followed by a blank. For this cause an IF statement is frequently referred to as an IF sentence. Many times, we encounter situations where no action requires to be specified if the condition is true, but some actions are essential if the condition is false. In that situation, the NEXT SENTENCE phrase can be used for the then part and the else part can be written to point the actions needed. Likewise, the NEXT SENTENCE phrase can substitute the else part if no action is needed when the condition is false. The NEXT SENTENCE phrase shows that the control should pass to the statement which follows the IF sentence. Note that if no action requires to be specified for the else part, the ELSE NEXT SENTENCE phrase being optional, can be absent.
Though, the phrase ELSE NEXT SENTENCE may not be omitted in many cases. The illustrations below describe the use of IF statement.