<LABEL>
<LABEL>, an HTML 4.0 element supported by Netscape6 and MSIE, defines a set of text which is associated with a specific form element. For illustration, code below indicates that phrase "send more information" is associated with "moreinfo" checkbox as checkbox is within the <LABEL> element:
<HTML>
<BODY>
<LABEL FOR="moreinfo">
Send more information
<INPUT NAME="moreinfo" TYPE=CHECKBOX ID="moreinfo">
</LABEL>
</HTML>
FOR attribute is required in above illustration. Value of FOR must be the same as value of ID in the form field that label applies to.
You can also associate a <LABEL> with a field which is not within its contents using the FOR attribute.
Attribute for <SELECT>
TABINDEX = integer
TABINDEX is supported by Netscape 6 and MSIE 4.x higher.
Usually, when user tabs from field to field in a form (in a browser which allows tabbing, not all browsers do) tab order is the order in which fields appear in HTML code.
Although, sometimes you want tab order to flow a little differently. In that scenario, you can number the fields using TABINDEX. Tabs then flow in order from one with the lowest TABINDEX to highest.
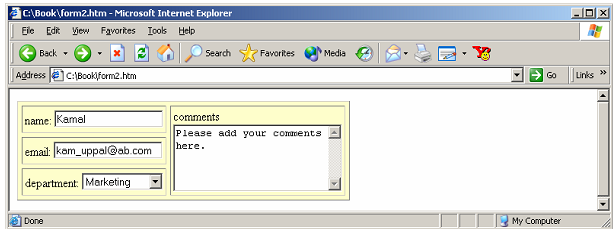
Code below explains this:
<HTML>
<BODY>
<TABLE BORDER CELLPADDING=3 CELLSPACING=5
BGCOLOR="#FFFFCC">
<TR>
<TD>name: <INPUT NAME="realname" TABINDEX=1></TD>
<TD ROWSPAN=3>comments<BR>
<TEXTAREA COLS=25 ROWS=5
TABINDEX=4></TEXTAREA></TD></TR>
<TR> <TD>email: <INPUT NAME="email" TABINDEX=2></TD></TR>
<TR> <TD>department: <SELECT NAME="dep" TABINDEX=3>
<OPTION VALUE="">...
<OPTION VALUE="mkt">Marketing
<OPTION VALUE="fin">Finance
<OPTION VALUE="dev">Development
<OPTION VALUE="prd">Production</SELECT></TD></TR>
</TABLE>
</HTML>
TABINDEX can be used with <A>, <INPUT>, <TEXTAREA>, and <BUTTON