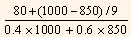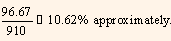Illustration
Consider a Rs.1,000 par value bond whose current market price is Rs.850. The bond carries a coupon rate of 8% and has a maturity period of 9 years. What would be the rate of return that an investor earns if he purchases the bond and holds till maturity?
Solution
The rate of return earned, also referred to as yield to maturity, is the value of kd in the following equation:
P0 = 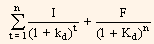
Rs.850 = 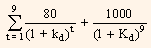
= Rs.80 (PVIFAkd%, 9 yrs) + Rs.1,000 (PVIFkd%, 9 yrs.).
Where,
I = Interest
F = Face value
kd = Cost of debt
P0 = Current market price.
To find out the value of kd in the above equation, several values of kd will have to be tried out in order to reach the input value. Therefore, to start with, consider a discount rate of 12% for kd for which the expression becomes equal to:
= Rs.80 (PVIFA 12%, 9 yrs) + Rs.1,000(PVIF12%, 9 yrs.)
= Rs.80 x 5.328 + Rs.1,000(0.361)
= Rs.426.24 + Rs.361 = Rs.787.24.
Since the above, value is less than the market price, we have to try with a less discounting rate (kd). So, let kd = 10%, then the equation becomes:
= Rs.80(PVIFA10%, 9 yrs.) + Rs.1,000 (PVIF10%, 9 yrs.)
= Rs.80 x 5.759 + Rs.1,000 x 0.424
= Rs.460.24 + Rs.424 = Rs.884.72
From the above, it is clear that kd lies between 10% and 12%. Now, we have to use linear interpolation in the range of 10% and 12%. kd is determined as follows:
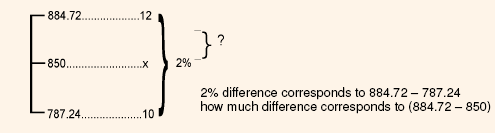
= 10% + (12 - 10%) 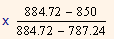
= 10% + 2% 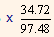
= 10% + 2% x 0.356
= 10% + 0.71
= 10.71%
The yield to maturity is 10.71%.
An Approximation: As trial and error methods of calculation are tedious, the following approximation formula can be employed to find out the approximate YTM on a bond.
YTM = 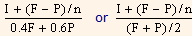
Where,
YTM = Yield to maturity.
I = Annual interest payment.
F = Par value or redemption value of the bond.
P = Current market price of the bond.
N = Years to maturity.
Therefore,
YTM =