Can the operand expression in an ORG statement contains forward references? If so, outline how the statement can be processed in a two-pass assembly scheme.
ORG that is origin is an assembler directive that
- Indirectly assign values to symbols
- Reset the location counter to the given value-ORG value
- Value can be: other symbol, constant or expression
- No forward-reference
Assemblers scan the source program, producing machine instructions. Occasionally, the assembler reaches a reference to a variable that has not yet been explained. It is referred to as a forward reference problem. This is resolved in a two-pass assembler as given here:
In the first pass, the assembler simple firstly reads the source file, counting-up the number of locations as each instruction will take, and makes a symbol table in memory which lists all the defined variables cross-referenced to their connected memory address. In the second pass, the assembler substitute's opcodes for the mnemonics and names of variable are replaced by the memory locations acquired from the symbol table.
Consider the illustrated program
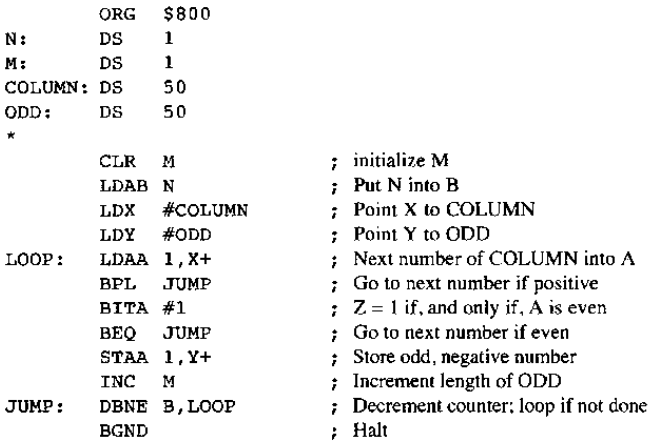
On the first pass, the ORG statement puts the location counter to $800. Therefore the label N has the value $800, the label COLUMN has the value $802, the label M has the value $801 and the label ODD has the value $834. Hence the instruction CLR M will get three bytes, the instruction LDAB N will get three bytes and same forth. Likewise, we see that the first byte of instruction we observe that the first byte of instruction
LOOP: LDDA 1, X+
IT will be at location $872. Therefore the symbolic address LOOP contain the value $872 and so on. In this continuing way, we come to
BPL JUMP
Such program searches the array COLUMN seem for odd, negative, one-byte numbers, that then are stored in array ODD. The length of COLUMN is N and the length of ODD is M, that the program computes. We do not know the second byte of such instruction since we do not know the value of the address JUMP still. (It is termed as a forward reference, by using a label whose value is not still known.) Conversely, we can leave this second byte undetermined and proceed till we see that the machine code for DBNE is put in location $87f, therefore giving JUMP the value $87f.
If we continue our first pass downward then we allocate three bytes for DBNE B,LOQP.
We do not get this instruction's offset still, even if we already know the value of LOOP.
Scanning by the program again, that is the second pass, we can fill in each bytes, including those not found the first time through, for the instructions as BPL JUMP, BEQ JUMP and DBNE B,LOOP. Now, all object code can be produced.