An un- ordered student file has 20,000 records stored on a disk having the Block size as 1 K. Suppose that each student record is of 100 bytes, the secondary index field is of 8 bytes, and block pointer is also of 8 bytes, find how many block accesses on average may be saved on using secondary index on enrolment number.
Answer:
Number of accesses without using Secondary Index:
Number of records in the file = 20000
Block size = 1024 bytes
Record size = 100 bytes
Number of records per block = integer value of [1024 / 100] = 10
Number of disk blocks acquired by the file = [Number of records / records per block]
= [20000/10] = 2000
As the file is un-ordered any search on an average will require about half of the above blocks to be accessed. Thus, average number of block accesses = 1000
Number of accesses with Secondary Index:
Size of an index entry = 8+8 = 16 bytes
Number of index entries that can be stored per block
= integer value of [1024 / 16] = 64
Number of index entries = number of records = 20000
Number of index blocks = ceiling of [20000/ 64] = 320
Number of index block transfers to find the value in index blocks = ceiling of [log2320] = 9
One block move will be needed to get the data records using the index pointer after the needed index value has been located. So total number of block transmits with secondary index = 9 + 1 = 10
Therefore,, the Secondary index would save about 1990 block transmit for the given case. This is a huge saving compared to primary index. Please also compare the size of secondary index to primary index.
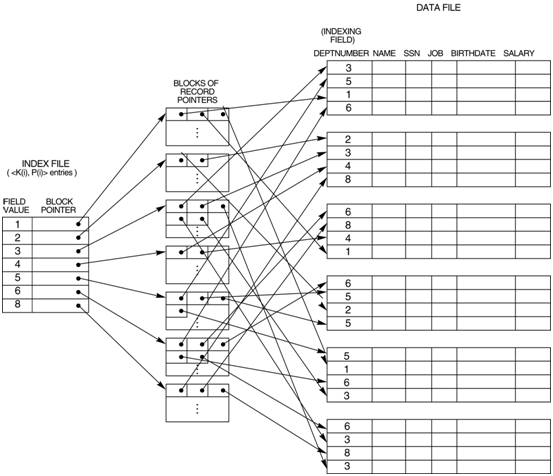
Let us now see an illustration of a secondary index that is on an attribute that is not an alternate key.