Horizontal Curves:
When a vehicle of mass m moves on a curve of radius R with a speed of v (m/sec) (as shown in Figure 1) it is subjected to a centrifugal force equal to:
mv2/ R
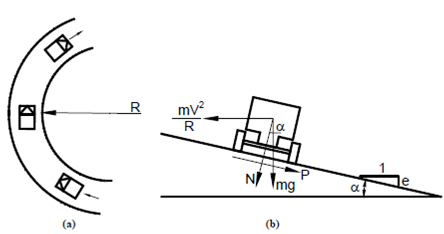
Figure: Forces Acting on a Vehicle on a Curve
where m = Mass of the vehicle,
v = Speed of the vehicle in metres/sec,
R = Radius of the curve in metres,
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81m/sec2),
P = Side friction force resisting the centrifugal force = N µ,
N = Normal force,
µ = Coefficient of lateral friction,
α = Angle of super-elevation, and
e = Rate of superelevation, tan α.
This is counteracted by the coefficient of lateral friction (μ) and the amount by which the road is raised (super-elevation, e). It can be shown that
v2/ gR = e + μ
Expressing v as V in Km/hr,
V2/127 R= e + μ
or R = V2/127 (e + μ)
The maximum comfortable value of e is 7 per cent (e = 0.07), and μ = 0.15.
Thus, R = V2/127 (0.07 + 0.15) = 0.0357 V2
For example, if a vehicle negotiates a National Highway (designed for V = 100 km/hr),
R = 0.0357 × 1002 = 357 or say 360 m.
In India, the actual value of the super-elevation to be provided on a curve is calculated on the assumption that it should counteract the centrifugal force developed at three-fourths the design speed. Thus,
V 2/127 R = e + μ
Putting μ = 0
V2/127 R= e
∴ e = (0.75 V) 2/127 R = V2/225 R
Thus, R =V2/225 e
The road has a normal camber (1.5 to 2.5 per cent depending upon the type of surface). If this value is substituted in the above equation, the value of the radius beyond which no superelevation is required is obtained. Thus, on a black-topped road with a camber of 2.5%, and a design speed of 100 Km/hr, the minimum radius beyond which no super- elevation is required is:
R = 100 × 100/225 × 0.025 = 1777 m, or say 1800 m