High Pressure Gas Hazards
When we consider the dangers of compressed gas in the lab, there are three main sources of danger as follows:
1) Sudden release of high pressure gas
2) Gas cylinders as unstable heavy objects
3) Inherent dangers of the contents of gas cylinders
It is advisable to know as to what general precautions should be taken when handling gases, or even to know the dangers of particular gases. None of this knowledge is of much use to you if you don't actually know what gas is inside the cylinder. The main indication is given on the shoulder of a cylinder where the name and chemical formula of the gas should appear. A secondary indication of the gas or its nature is given by colour coding as follows:
i) Ground colours - covering the entire cylinder body
ii) Colour bands - on the shoulder of the cylinder.
Figure: Gas cylinder with colour coding.
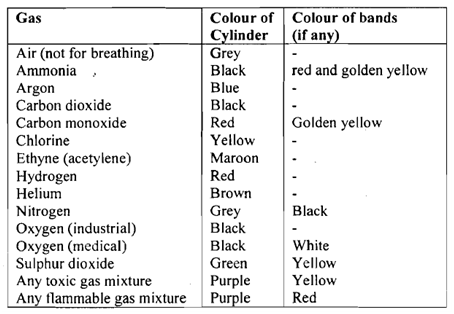
The ground colours tell you what the gas is, and the bands tell you something about the nature of the gas. Table 1 1.1 summarises the important markings which should be learnt by heart.
Table: Gas cylinder colour codes.
In addition to the colour codes, flammable gases are usually indicated by cylinders being fitted with a left-hand thread. Of course this indication is only of use when fitting a valve and regulator to a cylinder. However, you need to know which way to turn when removing the valve unit.