We will start by defining a new structure called Heap. Figure 3 illustrates a Binary tree.
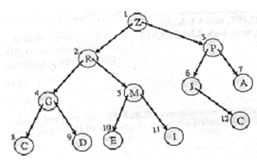
Figure: A Binary Tree
A complete binary tree is said to assure the 'heap condition' if the key of each node is greater than or equal to the key in its children. Therefore the root node will have the biggest key value.
Trees can be represented such as arrays, by first numbering the nodes (beginning from the root) from left to right. Then the key values of the nodes are assigned to array positions whose index is specified by the number of the node. For example, the corresponding array is depicted in Figure
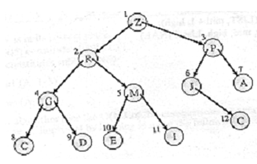
Figure: Array for the binary tree of figure
The relationships of a node can also be found out from this array representation. If a node is at position of j, its children will be at positions 2j & 2j + 1. Its parent will be at position +J/2+.
Assume the node M. It is at position 5. Therefore, its parent node is at position
5/2+ = 2 that means the parent is R. Its children are at positions 2 × 5 & (2 × 5) + 1, that means 10 + 11 respectively that means E & I are its children.
A Heap is a complete binary tree, wherein each node satisfies the heap condition, represented as an array.
Now we will study the operations possible over a heap and see how these can be combined to produce a sorting algorithm.
The operations on a heap work into 2 steps.
1. The needed node is inserted/deleted/or replaced.
2. The above operation may cause violation of the heap condition thus the heap is traversed and modified to rectify any such kind of violations.
Examples: Assume the insertion of a node R in the heap 1.
1. Initially R is added as the right child of J & given the number 13.
2. However, R > J. hence, the heap condition is violated.
3. Move R up to position six & move J down to position thirteen.
4. R > P. thus, the heap condition is violated still.
5. Swap R & P.
4. Now the heap condition is satisfied by all nodes to get the heap of Figure
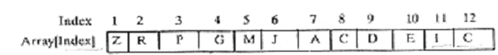
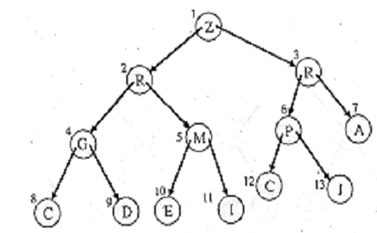
Figure: A Heap
This algorithm is guaranteed to sort n elements within (n log2n) time.
First we will see two methods of heap construction and then elimination in order from the heap to sort the list.
1. Top down heap construction
• Add items into an initially empty heap, satisfying the heap condition at all steps.
2. Bottom up heap construction
• Build a heap along the items in the order presented.
• From the right most nodes modify to satisfy the heap condition. We will reveal this with an example.
Example: construct a heap of the following using top down approach for heap construction.
PROFESSIONAL
Figure illustrates different steps of the top down construction of the heap.
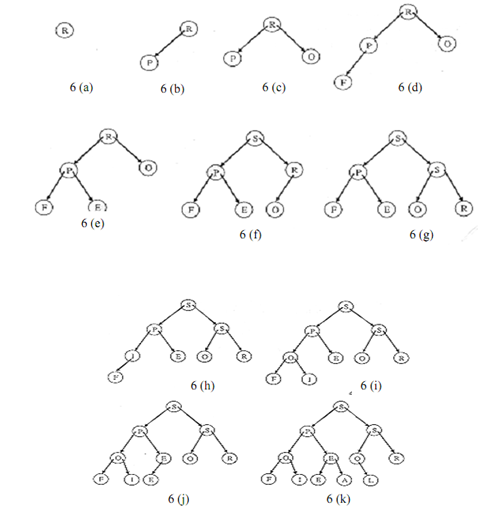
Figure: Heap Sort (Top down Construction)
Example: The input file is (2,3,81,64,4,25,36,16,9, 49). While the file is interpreted as a binary tree, it results in Figure. Another Figure shows the heap.
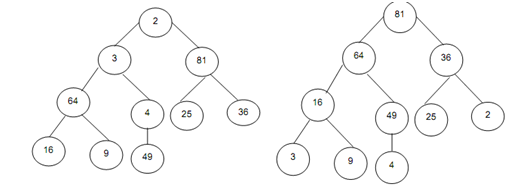
Figure: A Binary tree Figure: Heap of figure
Given figure illustrates several steps of the heap of above Figure as the sorting takes place.