Q. Describe the term hashing. Explain any two usually used hash functions. Explain one method of collision resolution.
Ans.
A hash table is a data structure in which the location or address of a data item is determined directly as a function of data item itself instead of by a sequence of comparison. Under ideal condition, the time needed to find a data item in a hash table is
0(1) ie. it is constant and documents does not depend on the number of data items stored in it.
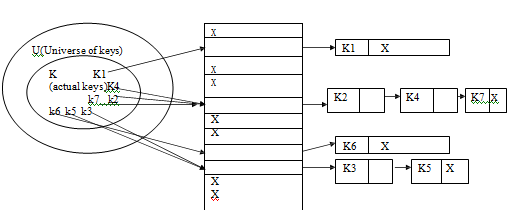
When the set of K of keys saved is much smaller than the universe U of all the probable keys, a hash table need much less storage spare than a direct address table.
Hash Function is described as follows
A hash function h is simply a mathematical or calculative formula that manipulates the key in some form to compute or calculate the index for this key in the hash table. Eg a hash function can split the key by some number, generally the size of the hash table and return remainder as the index for the key. Commonly, we say that a hash function h maps the universe U of keys into the slots of a hash table T[0....n-1]. This process of mapping keys to appropriate slots in a hash table is called as hashing.
A hash function h is generally a mathematical or calculative formula that manipulates the key in some form to compute or calculate the index for this key in the hash table. Eg a hash function can split the key by some number, generally the size of the hash table and return remainder as the index for the key. Commonly, we say that a hash function h maps the universe U of keys into slots of a hash table T[0....n-1]. This process of mapping keys to appropriate slots in a hash table is called as hashing.
(a) Division Method is given as follows:- In this process, key K to be mapped into one of the m states in the hash table is separated by m state in the hash table is divided by m and the remainder of this separation taken as index into the hash table. The hash function is as follows
h(k) = k mod m
where mod is the modules operations performed.
(b) Multiplication Methodis described as: The multiplication method or technique operates in 2 steps. In the 1st step the key value K is multiplied by a constant A in the range O
h(k) = [m (K A mod 1)]
Methods of Collision Resolution are stated below
1) Collision Resolution by the separate chaining
2) Collision Resolution by an open addressing
1) In this scheme all elements whose key hash to same hash table slot are put in a related list. Thus the slot in the hash table comprises a pointer to the head of the related list of all the elements that hash to value i. If there is no such element that hash to value I , the slot I comprises the NULL value ( pictures as X)