Hard Disk Technology:
Figure of a computer hard disk drive
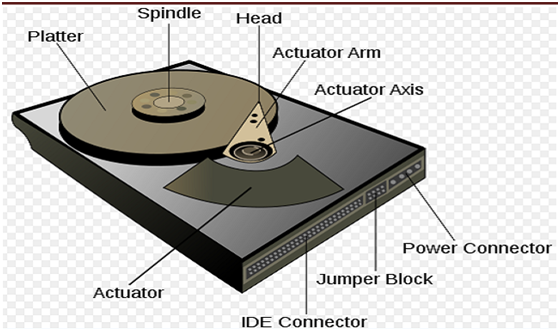
HDDs record data by magnetizing ferromagnetic material directionally, to represent either a 1 or a 0 binary digit. They read data again by detecting the magnetization of the material. A classic HDD design consists of a spindle that have one or more flat circular disks known as platters, onto which the data is recorded. The platters are made by non-magnetic material, typically glass or aluminum alloy, and are coated with a thin layer of magnetic material, usually 10-20 nm in thickness having an outer layer of carbon for protection.
The platters are spun at very high speeds. Information is written to a platter as it rotates past devices known as read-and-write heads that operate closely (tens of nanometers in new drives) above the magnetic surface. The read-and-write head is utilized to modify and detect the magnetization of the material instantly under it. There is 1 head for each magnetic platter surface on the spindle, mounted on a general arm. An actuator arm (or access arm) moves the heads on an arc (roughly radically) across the platters as it spin, permitting each head to access almost the whole surface of the platter as it spins. The arm is moved by using a voice coil actuator or in some older designs a stepper motor.
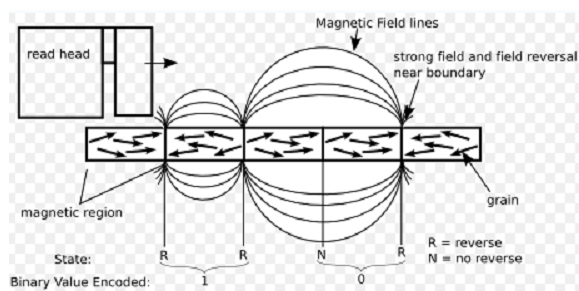
The magnetic surface of every platter is conceptually divided into several small sub-micrometer-sized magnetic regions, each of which is utilized to encode a single binary unit of information. firstly the regions were oriented horizontally, but starting regarding 2005, the orientation was changed to perpendicular. Because of the polycrystalline nature of the magnetic material each of these magnetic regions is formed of a few hundred magnetic grains. Magnetic grains are usually 10 nm in size and each form a single magnetic domain. Each magnetic region in whole forms a magnetic dipole which produced a highly localized magnetic field nearby. A write head magnetizes a region by producing a strong local magnetic field. Early HDDs which is used an electromagnet both the reason to magnetize the region and to then read its magnetic field using electromagnetic induction. Later versions of inductive heads had metal in thin film heads and Gap (MIG) heads. As data thickness increased, read heads by using magneto resistance (MR) imply to use; the electrical resistance of the head changed according to the strength of the magnetism from the platter. Afterward development made use of spin tonics; in these heads, the magneto resistive cause was much higher than in earlier types, and was dubbed "giant" magneto resistance (GMR). In present heads, the write and read elements are separate, but in near proximity, on the head piece of an actuator arm. The read element is in general magneto-resistive whereas the write element is typically thin-film inductive.
HD heads are kept from touching the platter surface by the air that is extremely near to the platter; that air moves at, or near to, the platter speed. The playback head and record are mounted on a block known a slider, and the surface next to the platter is shaped to keep it only barely out of contact. It's a type of air bearing.
In modern drives, the short size of the magnetic regions built the hazard that their magnetic state must be lost due to thermal effects. To overcome from it the platters are coated with 2 parallel magnetic layers, separated from a 3-atom-thick layer of the non-magnetic element ruthenium, and the 2 layers are magnetized in opposite orientation, hence reinforcing each other. Another technology used to defeat thermal effects to permit greater recording densities is perpendicular recording; first shipped in the year 2005, as of year 2007 the technology was used in many HDDs.
The granule boundaries turn out to be very essential in HDD design. Due to the grains are very short and near to each other, so the coupling amongst adjacent grains is very powerful. When 1 grain is magnetized, the neighboring grains tend to be aligned parallel to it or demagnetized. Then both firmness of the data and SNR ratio will be sabotaged. A clear grain boundary can decline the coupling of the grains and subsequently increase the SNR ratio. In longitudinal recording, the single-domain grains have uniaxial anisotropy with simple axes lying in the film plane. The end result of this arrangement is that adjacent magnets resist each other. So the magneto static energy is so high that it is hard to increase areal density. Perpendicular recording media, alternatively, has the easy axis of the grains oriented perpendicular to the disk plane. Adjacent magnets magnetize to each other and magneto static energy are much slower. So, much higher areal density can be achieved in perpendicular recording. Another exclusive feature in perpendicular recording is that a soft magnetic under layer are incorporated into the recording disk. This under layer is utilized to conduct writing magnetic flux so that the writing is more proficient. It will be discussed in writing process. So, a higher anisotropy medium film, such as L10-FePt and rare-earth magnets, may be utilized.