HALOGENS
The halogen group (17) is the biggest electronegative in the periodic table, and all elements readily form halide ions X-. Trends in chemistry resemble those collect in other groups. Fluorine is minimized to an octet of valence electrons. It is the biggest reactive and electronegative of all elements and usually (as with oxygen) brings out the highest oxidation state in other elements: as where no corresponding oxide is known include AuF5 and PtF6.
Cl and F are moderately abundant elements, principal sources being halite NaCl and fluorite CaF2, from which the very electronegative elements are produce by electrolysis. Bromine is mainly collect by oxidation of Br- found in salt water; iodine performs as iodates such as Ca(IO3)2. Astatine is radioactive and only minute amounts are present in nature.
Chlorine is used (as ClO2 and ClO-) in bleaches and is an important industrial chemical, other major need (as with all the halogens) being in the builder of halogenated organic compounds. The elements form diatomic molecules, Cl2 and F2 being gases at normal pressure and temperature, Br2 liquid and I2 solid. They combine directly with most other elements and are great oxidizing agents, although reactivity declines down the group.
The redox behavior is widely pH dependent but is also influenced by kinetic factors. It may be seen that Br2 and Cl2 disproportionate in alkaline solution. The thermodynamically expected products are X- and but the hypochlorite ion ClO- is build in cold conditions, and further disproportionation performs on heating.
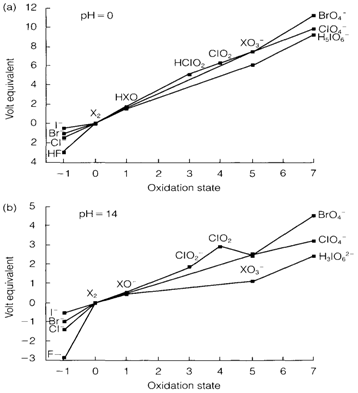
Fig. Frost diagrams for the halogens in aqueous solution at pH=0 (a) and pH=14 (b). X represents any halogen, except F for positive oxidation
states.
The perhalic acids and their anions are rigid oxidizing agents, normally which is not thermodynamically stable in aqueous solution. They do have relievable kinetic stability. Organometallic cations or perchlorates of organic are very dangerous as they can appear stable, but can explode unpredictably with full force.