GYROSCOPES:
PRINCIPLES
Gyroscopes are rotating masses (usually cylindrical in form) which are deliberately employed because of the particular properties which they demonstrate. (note, however, that any rotating mass may demonstrate these properties, albeit unintentionally). Basic concepts can be gained by reference to a hand-held bicycle wheel. Imagine the wheel to be stationary; it is easy to tilt the axle one way or another.
RIGIDITY
Now rotate the wheel. Because the mass of the wheel is rotating, it now has angular momentum. Two properties now become apparent.
The rotating wheel is now difficult to tilt, this is resistance is termed Rigidity.
PRECESSION
If sufficient force or torque is applied to tilt the wheel, the manner or direction in which it tilts or moves is interesting.
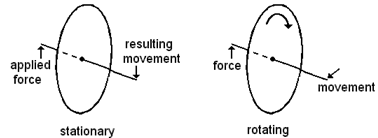
The movement of a gyroscope resulting from an applied torque is known as Precession.
To calculate the manner or direction in which a gyroscope will precess, a simple rule applied.
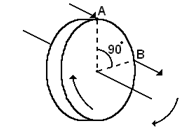
Assuming the force is applied at A, then the gyroscope will behave as though the force had been applied at a point B, 90º onward in the direction of rotation.
TORQUE
The torque required to cause precession, or the rate of precession resulting from applied torque, depends on moment of inertia and angular velocity. Remember that direction of rotation will determine direction of precession.