Graphical Representation of Various Returns:
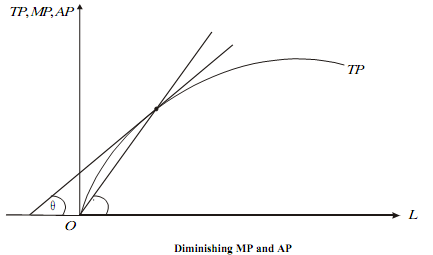
Diminishing Returns: If the TP curve is as shown in the adjacent Figure, then the MPL given by tanθ is throughout less than the APL given by tanθ�.
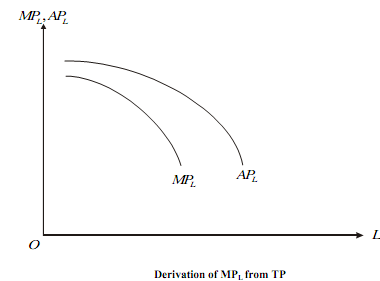
As APL is falling from the relation between MP and AP, MP < AP we have the adjoining Figure.
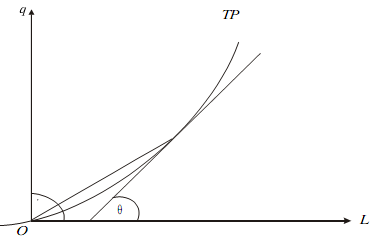
Increasing Returns Here APL rises and tan � < tanθ , for all L. Therefore, MP > AP. This is shown in the adjacent Figure.
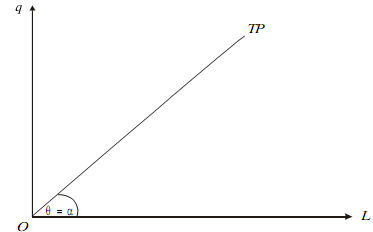
Constant Returns Here, APL is constant and tanθ = tan �, therefore, MPL = APL as is shown by a horizontal straight line in the next Figure(a,b)
The TP curve is such that upto point A, MP is rising and so is AP and MP > AP, as shown in the diagram below. Beyond point A, MP falls but AP rises, till the two are equated at point B. At B, AP is maximised. AP falls beyond the point B. At point C, the TP curve flattens out and therefore, MP = 0. Beyond C, MP is negative and AP is falling. Therefore, in the case of non-proportional return, both MP and AP rise, initially. MP reaches a maximum earlier than AP. When they both are equated, AP is maximised. Finally, there is a situation where both are falling. Depending on the nature of MP and AP, the production process can be divided into three stages - I, II, and III, as shown in Figure.
Characteristics of the three stages are :
Stage I: MP > 0, AP rising, thus MP > AP
Stage II: MP > 0, AP falling, thus MP < AP
Stage III: MP < 0, AP falling
In stage I, by adding one more unit of L, the producer can increase the average productivity of all the units. Thus, it would be unwise for the producer to stop production in this stage.
In stage III, MP < 0, so that by reducing the L input, the producer can increase the total output and save the cost of a unit of L. Therefore, it is impractical for a producer to produce in this stage.
Hence, stage II represents the economically meaningful range. This is so because here MP > 0 and AP > MP. So that an additional L input would raise the total production. Besides, it is in this stage that the TP reaches a maximum.