Geometric Mean is defined as the nth root of the product of numbers to be averaged. The geometric mean of numbers X1, X2, X3.....Xn is given as
G = (X1 x X2 x X3 ..... Xn)1/n
The peculiar nature of growth over time is on account of compounding. For example, sales of a company were Rs.10 crore in 1997-98. In 1999-2000 they grew by 10% to Rs.11 crore. In 2000-2001 they grew by 20% to Rs.13.2 crore. The 20% growth rate applies to Rs.11 crore which includes the Rs.1 crore growth of the previous year. This is what is meant by compounding.
PROPERTY
The product of the quantity ratios will remain unchanged when the value of geometric mean is substituted for each individual value. This may be seen by substituting 0% for 100% and -50% in the above example.
USES
The geometric mean is used to find the average percent increase in sales, production, population or other economic or business series overtime.
Example 8
The following data relates to Voltas Ltd.
|
Year
|
Sales
Rs. in millions
|
|
1998-1999
|
6670.0
|
|
1999-2000
|
7794.6
|
|
2000-2001
|
9176.2
|
| The growth rate for the year 1999-2000 |
= |
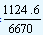 |
x 100 |
= 16.86% |
| The growth rate for the year 2000-2001 |
= |
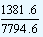 |
x 100 |
= 17.73% |
We can find that the sales of Voltas Ltd. has been increasing year by year, but at different growth rates. Now, the compounded annual growth rate can be arrived at by taking the geometric mean for the two quantity ratios.
|
G.M.
|
= |
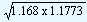 |
= |
1.1729 |
Growth rate = 1.1729 - 1 = 0.1729 or 17.29%
Thus, the compounded annual sales growth rate of Voltas Ltd. for the years 1998-99, 1999-2000 and 2000-2001 is 17.29%.
Geometric mean is most frequently used in finding out compound interest. The expression used in compound interest formula is
Pn = P0(1 + r)n
where,
Pn = The value at the end of period n
P0 = The value at the beginning of the period
r = Rate of compound interest per annum (expressed as a fraction)
n = Number of years.