Generation of steam at constant pressure:
Steam is pure substance. Like any other pure substance it can also be converted into any of the three states, that is, solid, liquid and gas. A system which comprises of liquid and vapour phases of water is a pure substance. Even if some of the liquid is vaporised or some vapour get condensed during this process, the system will be homogeneous chemically and unchanged in chemical composition.
Assume that unit mass of steam is generated beginning from solid ice at -10°C and 1atm pressure in cylinder and piston machine. The distinct regimes of heating are as given below:
Regime (A-B) : The heat given to ice increases its temperature from -10°C to 0°C. The volume of ice increases with the increase in temperature. Point B explains saturated solid condition. At point B the ice starts melting.
Regime (B-C): The ice melts into water at constant temperature and pressure. At point C the melting - process ends. There is sudden decrease in volume at temperature 0°C as the ice starts melting. It is a peculiar property of water because of hydrogen bonding.
Regime (C-D): The temperature of water increases heating from temperature 0°C to 100°C. The volume of water 1st decreases with an increase in temperature, reaches to its minimum at 4°C
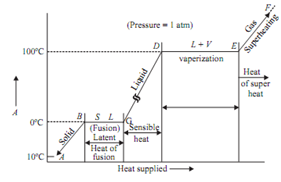
Point D shows saturated liquid condition.
Regime (D-E): The water starts boiling at D. The liquid starts getting into converted into vapour. The boiling stops at point E. Point E shows the saturated vapour condition at 100°C and 1 bar.
Regime (E-F): It shows the superheating of steam above saturated steam point. The volume of vapour increases quickly and it behaves as perfect gas. The difference between superheated temperature and the saturation temperature at a given pressure is called degree of superheat.
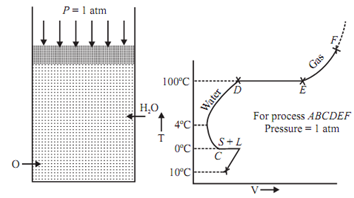
Point B, C, D, E are known as saturation states.
State B: Saturated solid state. State C and D: Both saturated liquid states.
State C is for hoar frost and state D is for vaporization.
State E: Saturated vapour state.
At the saturated state phase can get changed without any change in pressure or temperature.