General Perspective transformation w.r.t. an arbitrary center of projection
Suppose here that the COP is at C(a,b,c), as demonstrated in Figure.
By Figure, the vectors CP and CP' have the simila direction. The vector CP' is a factor of CP, which is CP'=α. CP
Hence, (x'-a)= α.(x-a) z
(y'-b)= α.(y-b)
(z'-c)= α.(z-c)
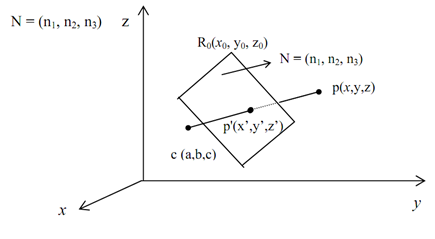
We know about the projection plane passing via a reference point R0(x0,y0,z0) and consisting a normal vector N= n1I+n2J+n3K, satisfies the subsequent equation:
n1.(x-x0)+n2.(y-y0)+n3.(z-z0)=0
When P'(x',y',z') lies upon this plane then we have:
n1.(x'-x0)+n2.(y'-y0)+n3.(z'-z0)=0
now substitute the value of x', y' and z' then we have:
α= (n1.(x0-a)+n2.(y0-b)+n3.(z0-c))/( n1.(x-a)+n2.(y-b)+n3.(z-c))
=((n1.x0+n2.y0+n3.z0)-(n1.a+n2.b+n3.c))/(n1.(x-a)+n2.(y-b)+n3.(z-c))
=(d0-d1)/(n1.(x-a)+n2.(y-b)+n3.(z-c))
=d/(n1.(x-a)+n2.(y-b)+n3.(z-c))
Currently, d=d0-d1= (n1.x0+n2.y0+n3.z0) - (n1.a+n2.b+n3.c) shows perpendicular distance from center of projection, C to the projection plane.
In order to determine the general perspective transformation matrix so we have to proceed as given here:
Translate COP, C (a, b, c) to the origin. Now, R'0=(x0-a, y0-b, z0-c) turn sinto the reference point of the translated plane which is normal vector will remain similar.
By applying the general perspective transformation as Pper,N,R'o
Now translate the origin back to C as.
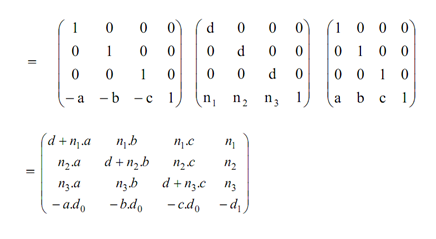
Here d = N.CR' 0 = d0 - d1 = (n1. x0 + n2. Y0 + n3.z0) - (n1.a+n2.b +n3.c)
= n1. (x0 - a) + n2. (y0 - b) + n3. (z0 - c)
And also d1 = n1.a + n2.b + n3.c