Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part II
Assume f ( x ) is a continuous function on [a,b] and also assume that F ( x ) is any anti- derivative for f ( x ) . Then,
∫baf ( x ) dx = F ( x )|b a= F (b ) - F ( a )
Recall that while we talk regarding an anti-derivative for a function we are actually talking regarding the indefinite integral for the function. Therefore, to evaluate definite integral the first thing which we're going to do is evaluate the indefinite integral for the function. It should describe the likeness in the notations for the indefinite & definite integrals.
Also notice that we need the function to be continuous within the interval of integration. It was also needs in the definition of the definite integral.
Next let's address the fact that we can utilize any anti-derivative of f ( x ) in the evaluation. Let's take an ultimate look at the given integral.
∫0 2 x2 + 1dx
Both are anti-derivatives of the integrand.
F ( x ) = 1/3 x3 + x and F ( x ) = (1/3) x3 + x - (18/31)
By using the FToC to evaluate this integral along with the first anti-derivatives gives,
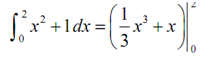
=(1/3) (2)3 + 2- ( (1/3)(0) 3 +0)
= 14 /3
Much easier than utilizing the definition wasn't it? Now let's utilizes the second anti-derivative to evaluate this definite integral.
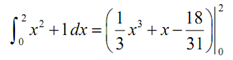
= (1/3) ( 2)3 + 2 - 18 /31- ( 1/3 (0)3 + 0 - 18/31)
=(1/3)(2)3+2-(18/31)-((1/3)(0)3+0-(18/31))
=14/3 - 18/31 + 18/31 = 14/3
The constant which we tacked onto the second anti-derivative canceled out in the evaluation step. Thus, while choosing the anti-derivative to utilizes in the evaluation procedure make your life simpler and don't bother with the constant as it will just end up canceling in the long run.
Also, note as well that we're going to contain to be very careful with minus signs and parenthesis along these problems. It's extremely easy to get in hurry & mess them up.
Let's begin our examples along with the following set designed to create a couple of quick points that are extremely important.
Example Evaluate following.
(a) ∫ 2 (1) y 2 + y -2 dy
(b) ∫ 2 (-1) y 2 + y -2 dy
(a) 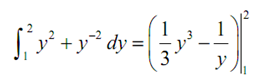
Following is the integral,
=( 1/3) 2 3 - (1/2)-((1/3)(1)3-(1/1))
=(8/3)-(1/2)-(1/3)+(1)
=(17/6)
(a) ∫ 2 (-1) y 2 + y -2 dy
This integral is to make a point. To do an integral the integrand has to be continuous in the range of the limits. In this case the second term will have division by zero at y = 0 and as y = 0 is in the interval of integration, that means it is among the lower & upper limit, this integrand is not continuous in the interval of integration & thus we can't do this integral.
Note as well that this problem will not stop us from doing the integral in (b) as y = 0 is not in the interval of integration.