Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part I
As noted through the title above it is only the first part to the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
The first part of this theorem us how to differentiate assured types of definite integrals and this also tells us regarding the very close relationship among integrals & derivatives.
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part I
If f ( x )is continuous on [a,b] then,
g ( x ) = ∫ax f (t ) dt
is continuous on [a,b] and this is differentiable on ( a, b ) and that,
g ′ ( x ) = f ( x )
An alternate notation for derivative portion of this is following,
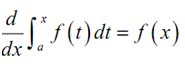
Example Differentiate following.
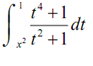
Solution
This one needed a little work before we can use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. The primary thing to notice is that the FToC needs the lower limit to be a constant & the upper limit to be the variable. Therefore, by using a property of definite integrals we can interchange the limits of the integral we only have to remember to add in a minus sign after we do that. Doing this we get,
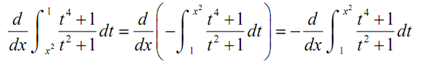
The next thing to notify is that the FToC also need an x in the upper limit of integration and we've got x2. To do this derivative we're going to required the following version of the chain rule.
d/dx ( g (u )) = d/dx ( g (u ))( du/dx) where u = f ( x )
Thus, if we let u= x2 we utilizes the chain rule to get,
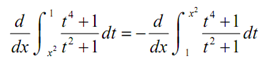
= -d/du ∫u1 (t4+1)/(t2+1)dt where u = x2
= (u4+1)/(u2+1) (2x)
= -2 x ((u4+1)/(u2+1))
The last step is to get everything back in terms of x.
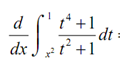
= -2x (( x2 )4 + 1)/ (x2 )2 + 1
= -2x(( x8+ 1)/ (x4+ 1)