The time has at last come to describe "nice enough". We've been using this term during the last few sections to explain those solutions which could be used to form a general solution and this is now time to officially describe it.
First, since everything that we're going to be doing here only needs linear and homogeneous we won't need constant coefficients in our differential equation. Thus, let's start with the subsequent IVP.
p (t ) y′′ + q (t ) y′ + r (t ) y = 0 ............. (1)
y (t0)= y0
y′ (t0) = y0′
Let's also assume that we have already got two solutions to this differential equation, y1(t) and y2(t). We identify from the Principle of Superposition as
y (t ) = c1 y1 (t) + c2 y2 (t) ................(2)
That will also be a solution to the differential equation. What we need to know is whether or not it will be a general solution. So as for (2) to be considered a general solution this must satisfy the general initial conditions in (1).
y (t0)= y0
y′ (t0) = y0′
It will also imply that any solution to the differential equation can be written in form of.
Therefore, let's see if we can get constants which will satisfy these conditions. First differentiate (2) and plug in the initial conditions.
y0 = y (t0) = c1 y1 (t0) + c2 y2 (t0)
y0′ = y′ (t0) = c1 y1′ (t0 ) + c2 y2′ (t0) .................. (3)
As we are assuming that we've already found the two solutions everything under this system is technically identified and so it is a system which can be solved for c1 and c2. It can be done in general using Cramer's Rule. By using Cramer's Rule provides the following solution.
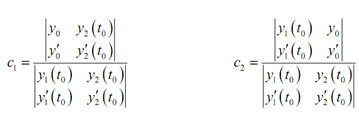
.........(4)
Here,
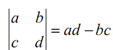
It is the determinant of a 2x2 matrix. If you don't identify about determinants which is okay, just utilize the formula that we've given above.
Now, (4) will provide the solution to the system (3). Remember that in practice we usually don't use Cramer's Rule to solve systems; we simply proceed in a straightforward way and solve the system using fundamental algebra techniques. Therefore, why did we use Cramer's Rule here so?
We used Cramer's Rule as we can use (4) to extend a condition which will permit us to determine when we can resolve for the constants. All three, here the denominators are the same that are use, of the quantities in (4) are just numbers and the only thing which will prevent us from in fact getting a solution will be while the denominator is zero.
The quantity in the denominator is termed as the Wronskian and is denoted as,
W(f,g) (t) =
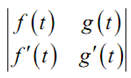
= f(t) g'(t) - g(t) f'(t)
So, assume that y1(t) and y2(t) are two solutions to (1) and that W ( y1 , y2)(t) ≠ 0. After that the two solutions are termed as a fundamental set of solutions and the general solution to (1) is
y (t ) = c1 y1 (t ) + c2 y2 (t )
We know here what "nice enough" means. Here two solutions are "nice enough" if they are a basic set of solutions.
Therefore, let's check one of the claims which we made in a previous section. We'll leave another two to you to check if you'd like to.