Functional Dependency
Consider a relation R that has 2 attributes A and B. The attribute B of the relation is functionally dependent on the attribute A if and only if for every value of A, no more than one value of B is related. In differet words, the value of attribute A uniquely shows the value of attribute B and if there were various tuples that had the similar value of A then all these tuples will have an identical value of attribute B. That is, if t1 and t2 are two tuples in the relation R where t1(A) = t2(A), then we must have t1(B) = t2(B).
Both, A and B require not be single attributes. They could be any subsets of the attributes of a relation R. The FD among the attributes can be written as:
R.A →R.B or easily A → B, if B is functionally dependent on A (or A functionally gives B). Please note that functional dependency does not imply a one-to-one relationship among A and B.
For example, the relation in Figure, whose dependencies are given in Figure, can be written as:
Enrolmentno →Sname Enrolmentno → Address Cno →Cname
Cno → Instructor
Instructor →Office
These functional dependencies entail that there can be only single student name for every Enrolmentno, only one address for each student and only one subject name for each Cno. It is of course possible that various students may have the similar name and various students may live at the similar address.
If we take Cno Æ Instructor, the dependency implies that no subject can have more than single instructor (maybe this is not a very realistic assumption). Functional dependencies thus place constraints on what information the database may store. In the instance above, you may be wondering if the following FDs hold:
Sname → Enrolmentno (1)
Cname →Cno (2)
Certainly there is nothing in the given situation of the database relation presented that contradicts the functional dependencies as over. Though, whether these FDs hold or not would depend on whether the college or university whose database we are allowing for duplicate course names and student names. If it was the activity policy to have unique course names than (2) holds. If duplicate student names are feasible, and one would think there always is the possibility of two students having exactly the name, then (1) does not hold.
An easy example of the functional dependency over is when A is a primary key of an entity (e.g., enrolment number: Enrolment no) and B is some one-valued property or attribute of the entity (e.g., student name: Sname). A →B then must always hold. (Why?)
Functional dependencies also occur in relationships. Suppose C is the primary key of an entity and D is the primary key of another entity. Let the two entities have a relationship. If the relationship is one-to-one, we have to do both C → D and D → C . If the relationship is many-to-one (Con many side), we would have C → D but not D →C . For many-to-many relationships, no functional dependencies grasp.
For example, let consider the following E-R diagram
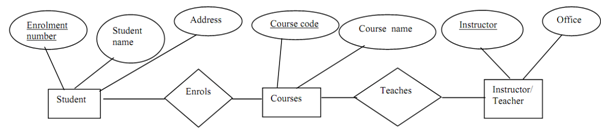
Figure: E-R diagram for student course Teacher
In the ER diagram as over, the following FDs exist: