When a manager measures the interest rate exposure, he would be interested in analyzing the exposure to a set of changing interest rate. The process of re-valuation of a bond or bond portfolio for a given interest rate change scenario is known as full valuation approach or scenario analysis.
For example, assume that a fund manager has Rs.1 crore par value position in a 12% coupon 25 years option free bond. Current value of the bond at 8% yield to maturity is Rs.142.70. To assess the exposure due to rise in the yield, the fund manager decides to look at how the bond value will change with the change in the yield. Let us take into consideration the following scenarios:
-
When the yield increase is by 75 basis points, then the new yield is 8% + 75 basis points = 8.75%.
-
When the yield increase is by 150 basis points, then the new yield is 8% + 150 basis points = 9.5%.
-
When the yield increase is by 300 basis points, then the new yield is 8% + 300 basis points = 11%.
The change in the market value of the bond position due to rise in the yield is given in Table 1.
Table 1: Full Valuation Approach to Assess the Interest Rate Risk of Bond Position
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change (bps)
|
New Yield
(%)
|
New Price
(Rs.)
|
New Market Value (Rs.)
|
% Change in the Market Value
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
8
|
142.70*
|
1,426,991,048
|
-
|
|
1
|
75
|
8.75
|
132.58
|
1,325,809,791
|
-7.09
|
|
2
|
150
|
9.50
|
123.59
|
1,235,939,443
|
-13.39
|
|
3
|
300
|
11.00
|
108.42
|
1,084,217,447
|
-24.02
|
* New Prices = 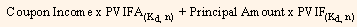
% Change in Market Value = 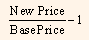
= 12 PVIFA(8.75%, 25) + 100 PVIF(8.75%, 25)
= 120.3 + 12.28 = 132.58.
In the case of portfolio, each bond is valued for a given scenario and then the total value of the portfolio is computed for the scenario. For example, assume that the fund manager has got 2 option free bonds: (a) 12% coupon, 25-years bond (b) 7% coupon 5-years bond. He has one crore rupees par value long-term investment in a 12% bond. The current market price of this bond at 8% yield is Rs.142.70. He has Rs.50 lakh par value short-term investment in 7% bond. The current price of this bond at 6% yield is Rs.104.21. The fund manager wants to assess the exposure for the portfolio, having these two securities, in the event the yield of both bonds increases by 75, 150 and 300 basis points. The change in the market value of 7% and 12% bond is given in Tables 2 and 3 respectively. The Table 4 shows the market value of the portfolio and percentage change in the market value of the portfolio.
Table 2: Market Value of the 5-years 7% Bonds for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change
(bps)
|
New Yield
(%)
|
New Price
(Rs.)
|
New Market Value (Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
6
|
104.21
|
521,061,819
|
|
1
|
75
|
6.75
|
101.03
|
505,159,738
|
|
2
|
150
|
7.50
|
97.98
|
489,885,288
|
|
3
|
300
|
9.00
|
92.22
|
461,103,487
|
Table 3: Market Value of the 25-years 12% Bonds for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change (bps)
|
New Yield
(%)
|
New Price
(Rs.)
|
New Market Value (Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
8
|
142.70
|
1,426,991,048
|
|
1
|
75
|
8.75
|
132.58
|
1,325,809,791
|
|
2
|
150
|
9.50
|
123.59
|
1,235,939,443
|
|
3
|
300
|
11.00
|
108.42
|
1,084,217,447
|
Table 4: Market Value of the Bonds Portfolio for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change (bps)
|
Market Value of
|
% Change in the Market Value
|
|
Bond 1
(Rs.)
|
Bond 2
(Rs.)
|
Portfolio
(Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
521,061,819
|
1,426,991,048
|
1,948,052,867
|
-
|
|
1
|
75
|
505,159,738
|
1,325,809,791
|
1,830,969,529
|
-6.01
|
|
2
|
150
|
489,885,288
|
1,235,939,443
|
1,725,824,731
|
-11.41
|
|
3
|
300
|
461,103,487
|
1,084,217,447
|
1,545,320,934
|
-20.67
|
In the previous example, we have seen that yield of both the bonds change by the same number of basis points. Now we will see one more example where yield curve of both the bonds does not change in parallel fashion.
We will take the previous example with certain modification. Let us say the yield of both bonds changes in the following manner:
Table 5
|
Scenario
|
Change in yield of
5-years bond (bps)
|
Change in yield of
25-years bond (bps)
|
|
1
|
75
|
35
|
|
2
|
150
|
95
|
|
3
|
300
|
160
|
Now we will see how market value of these bonds and the portfolio containing these bonds change. Tables 6 and 7 show the market value of the 5-years and 25-years bond in different scenarios.
Table 6: Market Value of the 5-years 7% Bonds for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change
(bps)
|
New Yield
(%)
|
New Price
(Rs.)
|
New Market Value
(Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
6
|
104.21
|
521,061,819
|
|
1
|
75
|
6.75
|
101.03
|
505,159,738
|
|
2
|
150
|
7.50
|
97.98
|
489,885,288
|
|
3
|
300
|
9.00
|
92.22
|
461,103,487
|
Table 7: Market Value of the 25-years 12% Bonds for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change
(bps)
|
New Yield
(%)
|
New Price
(Rs.)
|
New Market Value (Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
8.0
|
142.70
|
1,426,991,048
|
|
1
|
35
|
8.35
|
137.83
|
1,378,257,177
|
|
2
|
95
|
8.95
|
130.08
|
1,300,806,436
|
|
3
|
160
|
9.60
|
122.47
|
1,224,725,873
|
Table 8 given below shows the market value and change in the market value of the bond in different scenarios.
Table 8: Market Value of the Bonds Portfolio for the Three Scenarios
|
Scenario
|
Yield Change (bps)
|
Market Value of
|
% Change in the Market Value
|
|
Bond 1
(Rs.)
|
Bond 2
(Rs.)
|
Portfolio
(Rs.)
|
|
Current Position
|
-
|
521,061,819
|
1,426,991,048
|
1,948,052,867
|
-
|
|
1
|
75
|
505,159,738
|
1,378,257,177
|
1,883,416,915
|
-3.32
|
|
2
|
150
|
489,885,288
|
1,300,806,436
|
1,790,691,724
|
-8.08
|
|
3
|
300
|
461,103,487
|
1,224,725,873
|
1,685,829,360
|
-13.46
|
Now we can say that full valuation approach can be used for any scenario to evaluate the exposure of a bond or portfolio due to change in interest rate. But the main drawback with this approach is that it is very time consuming for a portfolio having a large number of bonds; and even with a few bonds also it is the same as it is complex. Managers do not want to revalue the whole portfolio or a bond to know the exposure due to change in interest rate. They want one method which tells them how portfolio or a bond will change if rate changes. Before dealing with is it some other measures or approaches per valuation. Let us understand price volatility characteristics of bonds.