The full lifecycle framework
The objective of this section is to introduce the full lifecycle approach proposed by Berghout et al. (2002). This framework deals in an effective manner with project dynamics and management learning issues throughout the full lifecycle representing a chance for organizations willing to improve their state of IT costs and benefits management. This framework is one of the available methods which include informal assessments and that does not underestimate IT complexity. Next, the full lifecycle framework will be presented for introductory purposes.
IT projects are complex, since managing costs and benefits of IT projects involve risks and uncertainty. Risks and uncertainty decrease during the project. However, at the same time, possibilities to change the information systems also decrease. This phenomenon is called the 'IT management paradox" (Berghout et al. 2002). For example, when IT is already in use, risks are lower, even so, the possibilities are lower to adapt operational systems to new requirement (Ibid.). Moreover, from a cost/benefit view, the activity of exploiting IT represents 60%-80% of the overall lifecycle costs while the possibility to limit these costs or increase benefits is very small (Ibid.). Consequently, not only the development costs but the complete lifetime of IT costs should be evaluated in order to avoid building information systems that will not deliver enough benefits during its exploitation (Ibid.).
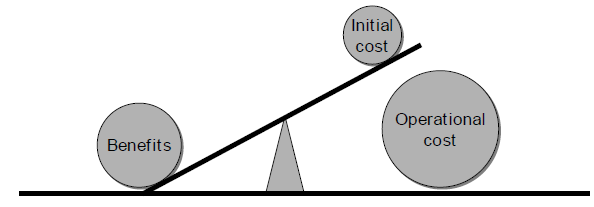
Figure 1: Incomplete benefit analysis (Berghout & Nijland 2002)
A lifecycle approach could help organizations with the assessment of "project dynamics" and the introduction of "management learning" in order to improve the state of management of cost/benefit in organizations. "Project dynamics" means that an organization might evaluate a project at any of several stages during its development and implementation: evaluation becomes a continuous and dynamic process. Thus, project should not only be evaluated at the initial stage but also through the stages of its lifetime (Farbey et al. 1999). "Management learning" means that a certain organization learn lessons from prior projects. As a result, relevant experiences can be reused for developing realistic and more accurate expectation for the approval of new IT investments (Ibid.).
Different approaches to lifecycle management exist and recognize the importance of managing IT investment throughout their full economic lifecycle (Swinkels 1997; Willcocks 1994; Thorp 1998. See similar full lifecycle propositions in appendix 8: Willcocks et al. 1997; Cio.de 2003). The full lifecycle management approach by Berghout & Nijland (2002) has been selected for this research because it is an effective scientific based approach for dealing with project dynamics and management learning issues. The full lifecycle management approach consists of several methods and techniques to manage information systems along the system's lifecycle (Ibid.). One of its techniques is the IT governance quick scan that can be used to visualize how organizations handle IT cost/benefit management.
The traditional full lifecycle comprises three major lifecycle activities: planning stage, development stage and exploitation stage. In
the planning stage the relevance of IT is examined in comparison to other possible business investments, new IT investments are
identified and their individual importance among all potential IT investments is established. In the development stage, the prioritized
investment proposals are designed, built, tested and implemented. Finally, in the exploitation stage, the information systems are
operated, controlled and maintained (Berghout & Nijland 2002).
Berghout & Nijland (2002) expand the traditional full lifecycle by including new stages within the lifecycle activities (see
figure 19 below) . The planning stage includes the prioritization of IT against non-IT and the prioritization between IT investments.
The development stage focuses on designing, building, testing and implementing of information systems investments. The exploitation
stage involves operating, maintaining and discarding operational information systems. The phase abandon indicates that IT does not
live forever. The different lifecycles stages have diverse costs and benefits and their calculation at each stage requires a profound
understanding from the performance of the other lifecycle phases.
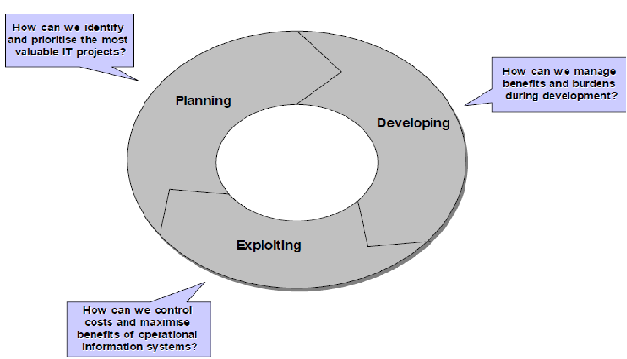
Figure 2: Three major lifecycle activities (Berghout & Nijland 2002)
In principle, evaluation will take place in each of the stages previously mentioned and involves different stakeholders such as
strategic management, IT management and line management. Firstly, a top-down, bottom-up and inside-out evaluation is conducted
for identifying interesting IT investments. Secondly, the evaluation continues in the justification stage by prioritizing investments.
Thirdly, the evaluation continues during the development stage by managing the costs, benefits and time schedule of projects.
Fourthly, the evaluation occurs during the exploitation stage by controlling functionality, by allocating costs and by managing
benefits. The evaluation in each stage is important because it provides useful information about the state of cost/benefit
management of present IT projects and because it allows organizations to create valuable knowledge for future IT projects
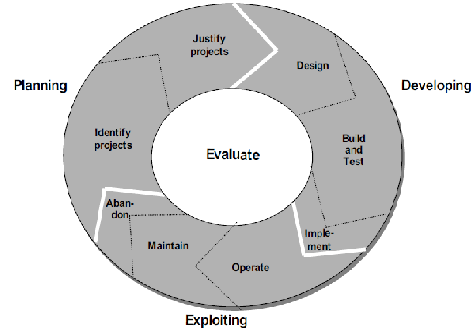
Figure 3: The Full Lifecycle Management in practice (Berghout et al. 2002)
The full lifecycle framework could make an important contribution for scholars and practitioners willing to obtain more benefits from IT. In chapter 2, it has been shown that CobiT 5 aims the realization of benefits from IT, for example , with the IT related goals "realise benefits from IT enabled investments and services portfolio" (CobiT 5 2012). Comparable to ISACA, the full lifecycle framework also pursues the realization of IT benefits. Furthermore, the full lifecycle framework includes additional aspects such as project dynamics and management learning issues which might improve the actual state of cost/benefit management in many organizations.