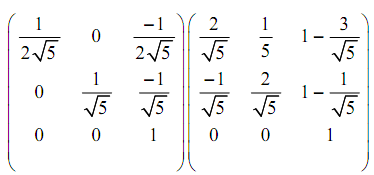Illustration: Find the normalization transformation N that uses the rectangle W (1, 1), X (5, 3), Y (4, 5) and Z (0, 3) as a window and also the normalized device screen like the viewport.
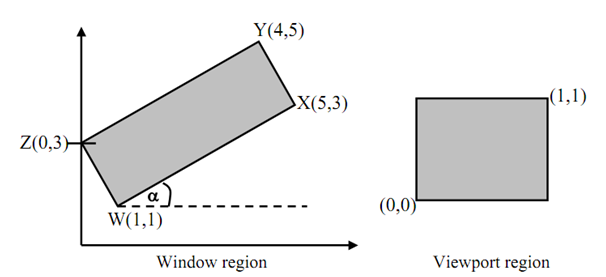
Figure: Example Transformations
Currently, we observe that the window edges are not parallel to the coordinate axes. Consequently we will first rotate the window regarding W hence it is aligned along with the axes.
Now, tan α= (3 -1)/(5-1) = 1/2
⇒ Sin α = 1 /√5; Cos α = 2/√5
Now, we are rotating the rectangle in clockwise direction. Consequently α is negative which is, - α.
The rotation matrix about W (1, 1):
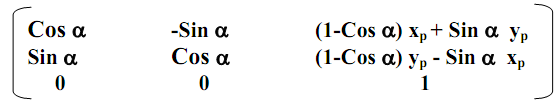
[TR.θ]W =
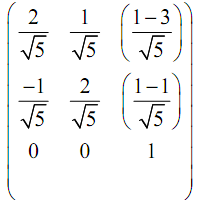
The x extent of the rotated window is the length of WX:
√(42 + 22) = 2√5
As same, the y extent is length of WZ that is,
√ (12 + 22) = √5
For scaling the rotated window to the normalized viewport we calculate sx and sy as,
sx = (viewport x extent)/(window x extent)= 1/2√5
sy = (viewport y extent)/(window y extent) = 1/√5
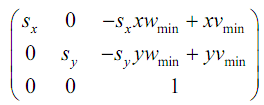
As in expression (1), the common form of transformation matrix showing mapping of a window to a viewport:
[T] =
Within this problem [T] may be termed as N as this is a case of normalization transformation with,
xwmin = 1 xvmin = 0
ywmin = 1 yvmin = 0
sx = 1/2√5
sy = 1/√5
Via substituting the above values in [T] which is N:
N =
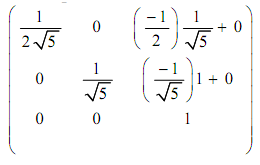
Here, we compose the rotation and transformation N to determine the needed viewing transformation NR.
NR = N [TR.θ]W =