File Organisation And Its Types
Just as arrays, trees, lists and other data structures are used to execute data Organisation in main memory, a number of planning's are used to support the Organisation of data in secondary memory. A file organisation is a method to organise data in the secondary memory. In this part, we are concerned with obtaining data representation for files on external storage devices so that need functions (e.g. update, retrieval,) may be carried out efficiently.
File Organisation is a way of arranging the records in a file when the file is accumulated on the disk. Data files are organized so as to facilitate access to records and to make sure their efficient storage. A tradeoff among these two requirements generally exists: if rapid access is needed, more storage is needs to make it possible. Selection of File Organisations is reliant on two factors as shown below:
- Typical DBMS applications require a small subset of the DB at any given time.
- When a portion of the data is required it must be located on disk, copied to memory for processing and rewritten to disk if the data was modified.
A file of record is likely to be accessed and modified in a various ways, and dissimilar ways of arranging the records enable dissimilar operations over the file to be carried out efficiently. A DBMS supports various file Organisation techniques. The main task of the DBA is to choose a good Organisation for every file, based on its type of use.
The definite organisation most suitable for any application will depend upon such factors as the part of external storage available, number of keys, types of queries allowed, mode of retrieval and mode of update. The Figure shows different file organisations based on an access key.
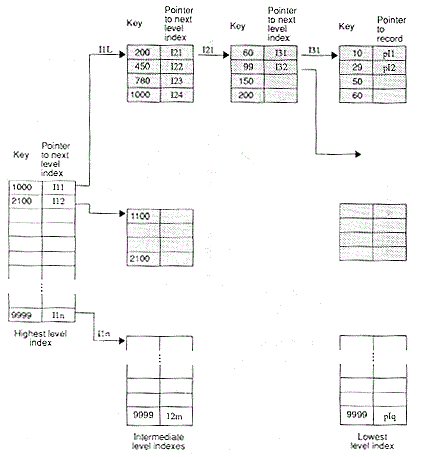
Figure : File Organisation techniques