Given two functions f(x) and g(x) which are differentiable on some interval I
(1) If W (f,g) (x0) ≠ 0 for some x0 in I, so f(x) and g(x) are linearly independent on the interval I.
(2) If f(x) and g(x) are linearly dependent on I so W(f,g)(x) = 0 for all x in the interval I.
Be very alert with this fact. This DOES NOT say as if W(f,g)(x) = 0 so f(x) and g(x) are linearly dependent! Actually it is possible for two linearly independent functions have a zero Wronskian!
This fact is utilized to quickly know linearly independent functions and functions which are liable to be linearly dependent.
Example 2: Verify the fact by using the functions,
a) f ( x ) = 9 cos ( 2x ) g ( x ) = 2 cos2 ( x ) - 2 sin 2 ( x )
(b) f (t ) = 2t 2 g (t ) = t 4
Solution:
(a) f ( x ) = 9 cos ( 2x ) g ( x ) = 2 cos2 ( x ) - 2 sin 2 ( x )
In this case if we calculate the Wronskian of the two functions we must get zero as we have already found that these functions are linearly dependent.
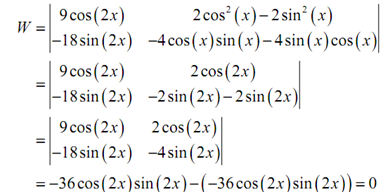
Therefore, we get zero as we must have. See the heavy use of trig formulas to simplify the work!
(b) f (t ) = 2t 2 g (t ) = t 4
Now there we know that the two functions are linearly independent and therefore we should find a non-zero Wronskian.
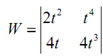
= 8t5 - 4t5 = 4t5
The Wronskian is non-zero as we estimated provided t ≠ 0. It is not a problem. As long as the Wronskian is not as identically zero for each t we are okay.