Explain what is Deamination Reaction ?
Deamination is a process by which N of amino acid is removed as ammonia (NH3). These reactions occur primarily in liver and kidney. The reaction is catalyzed by the following two enzymes:
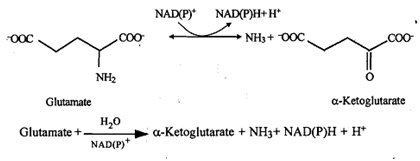
a) Glutamate dehydrogenase : Glutamate, as we have just seen above, is the major end product of transamination reactions. Further breakdown of glutamate occurs through the process of oxidative deamination. This is catalyzed by the enzyme L-glutamate dehydrogenase to form a-iminoglutaric acid, which on addition of a molecule of water forms NH, and aketoglutarate.
(This enzyme requires NAD(P) provided by vitamin B,(niacin) and is present in the mitochondrion). It is a reversible reaction as shown herewith:
b) Amino 'acid oxidase : D-amino acids present in the diet are efficiently metabolized by the liver by the enzyme amino acid oxidase. Amino acid oxidases are of two types. D-amino acid oxidase (breaks down D-amino acid) and L-amino acid oxidase (which acts on L-amino acids).
D-amino acid oxidase requires FAD (provided by vitamin B2) as the cofactor. It liberates NH, and a-keto acids, which can enter the general pathway of amino acid metabolism. However, the tissue proteins contain L-amino acids. These are catabolized by L-amino acid oxidases of liver and kidney which uses FMN (provided by vitamin B2) as the coenzyme and once again as earlier, liberates NH, and a-keto acids. However, the activity of L-amino acid oxidase in the body is very little and hence this type of oxidative deamination is not the major pathway of amino acid catabolism. Then, how are the amino acids broken down? Primarily by the transamination process. The amino acids are converted to glutamate as you have already learnt and then the glutamate is catabolised by L-slutamate dehydrogenase. The activity of this enzyme is very high in the body.
The discussion so far centered on the removal of amino groups. The end product formed being ammonia and the corresponding a-keto acids. What happens to this ammonia in the body? The next section focuses on the conversion of ammonia into urea. Let us see how this is done.