Explain the working of Skeletal Muscle?
Skeletal muscle is under voluntary control and is responsible for voluntary movements of body parts. Skeletal muscle is also called striated muscle because its composition results in a striped appearance. Each muscle fiber is formed by the fusion of embryonic muscle cells, or myoblasts, into a multinucleate structure called a syncytium. This syncytium is surrounded by a sarcolemma, similar to the plasma membrane of a uninucleate cell. A striated muscle fiber is composed of a bundle of 1,000 or more myofibrils, banded fibers formed from units called sarcomeres. Sarcomeres are bounded by Z-lines, thin structures that extend across each myofibril. Within the myofibril, filaments of actin alternate with thick filaments of myosin.
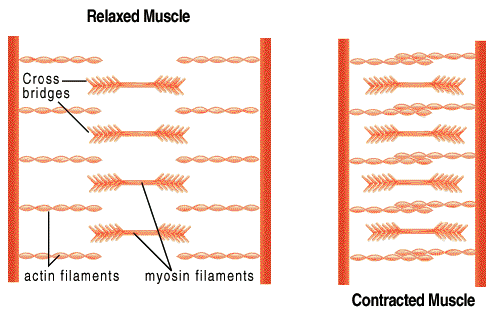
The mechanism of muscle contraction known as the sliding filament theory, proposed by Hanson and Huxley, suggests that progressive forming and breaking of bridges between polarized actin and myosin filaments pull the Z-lines closer together. Hydrolysis of ATP is required for both relaxation and contraction in skeletal muscle. After death of the individual, as ATP disappears from the body, the muscles lose their ability to either contract or relax, and become stiff, a condition known as rigor mortis.
A skeletal muscle contracts in response to signals from a motor neuron. As seen in the animation of muscle contraction, the "head" of the thick filament (myosin filament) attaches to the thin filament (actin filament) and "pulls" it toward the middle. In a muscle at rest, the myosin filaments are not able to attach to the actin filaments because the points of attachment are blocked by a filament of a protein called tropomyosin. The globular protein complex called troponin is able to bind to actin, calcium, and the fibrous protein tropomyosin. Troponin and tropomyosin normally block the attachment sites on actin, making actin unavailable for myosin to bind with. The only way myosin can attach to the actin filaments is if the binding sites are uncovered.
Nerves attach to the muscle at a modified postsynapstic area of the sarcolemma called a motor end plate. Nervous impulses sent to a group of motor end plates called a motor unit result in the release of calcium into the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. Calcium reacts with the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex, causing the attachment site to become uncovered. The myosin filaments are then able to bind with the actin filament and contraction occurs. Unlike smooth muscles, where the strength of contraction depends upon the degree of depolarization, striated muscle response is an all or none phenomenon; the force of contraction is proportional to the number of fibers stimulated.
Skeletal muscles responsible for movement of the limbs can be classified according to their function. Those which cause the joint to close up are flexors. Their opposite, or antagonistic muscles are called extensors, which cause the joint to stretch out. For example, biceps in the arm are flexors, while triceps extending from the shoulder to the elbow are extensors. Adductor muscles move a limb toward the body, while abductors move it away from the body.
The point of attachment of a flexor or extensor on the moving bone is called the insertion, and the point of attachment on the stationary bone is the origin. Voluntary skeletal muscles are attached to bones either directly or by means of straps of connective tissue called tendons. Movable joints are held together by ligaments, flexible bands of connective tissue, that hold muscles and tendons in place.