Explain the working of a 2-bit digital comparator with the help of Truth Table.
Ans.
Digital comparator is a combinational circuit which compares two numbers, A and B; and evaluates their relative magnitudes. The outcome of the comparison is given by three binary variables which indicate whether A = B or A > B or A < B.
Comparators can be implemented for comparing multi-bit numbers. Figure (a) demonstrates the block diagram of an n-bit comparator. This acquires two n-bit numbers A and B as inputs and the outputs are A = B, A > B and A < B. Depending on the relative magnitude of the two numbers, one of the outputs will be HIGH. Table no6.2 provides the truth table of a 2-bit comparator.
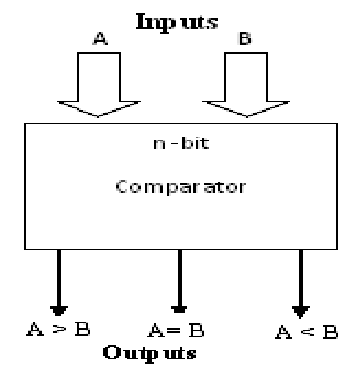
Fig.(a)block diagram of n bit compartor
(I) If the magnitude of the inputs A and B are equal (that is, A = B): see two numbers, A and B as inputs along with two digits each that is, A1, A0 and B1, B0. The two numbers are equivalent if all pairs of significant digits are equal that is, if A1 = 0, A0 = 0, B1 = 0, B0 = 0, then A1 = B1 and A0 = B0. For illustration if A1 = 0, A0 = 0, B1 = 0, B0 = 0, then pairs of significant digits that is, A1 = B1 = 0 and A0 = B0 =0. Output for this combination turns into 1 for A = B and 0 for A < B and A > B. It is specified in the Truth Table.
(II) If the magnitude of the input A is greater than or less than B (that is, A > B or A < B): To find out if A is greater than or less than B, we inspect the relative magnitude of pairs of significant digits starting from the most significant position. If the two digits are equivalent, we compare the subsequent lower significant pair of digits. The comparison of these continues till a pair of unequal digits is reached.
(i)If the input A is greater than B (that is, A > B): If the consequent digit of A is 1 and that of B is 0, we terminate that A > B. For illustration if A1 = 0, A0 = 1, B1 = 0, B0 = 0, then pairs of significant digits are A1 = B1 =0, and A0 (that is, digit 1) > B0 (that is, digit 0). It is illustrated in the Truth Table.
(ii) If the input A is less than B (that is, A < B): If the consequent digit of A is 0 and B is 1, we determine that A < B. For illustration if A1 = 0, A0 = 0, B1 = 0, B0 = 1, then pairs of significant digits are A1 = B1 =0, and A0 (that is, digit 0) < B0 (that is, digit 1). It is illustrated in the Truth Table.
|
Inputs
|
|
|
|
Outputs
|
|
|
A0
|
B1
|
B0
|
A > B
|
A = B
|
A < B
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
Table no.2 Truth Table of a 2-Bit Comparator