Explain the Thermodynamics - Heat and Work
Thermodynamics is an area of science which looks at how changes in energy, work and the flow of heat influence each other. It can explain the workings of an internal combustion engine, a refrigerator and the Sun.
The First Law of Thermodynamics is another way of stating the law of conservation of energy. The heat supplied to a system is equal to the increase in internal energy of the system plus the work done by the system.
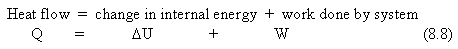
where all three quantities are measured in joules. The sign conventions are that Q is + if you add heat to the system and - if you remove heat from the system; U is + if you add internal energy to the system and - if you remove energy from the system; W is + if the work is done by the system, and - if work is done on the system.
James Prescott Joule showed that heat, and the change in temperature it can cause, are forms of energy. By constructing an experiment to measure the temperature change in water due to work done on it by stirring, he showed that the loss of gravitational potential energy by dropping a weight was turned into various forms of energy.
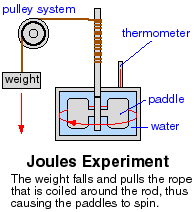
It was converted into kinetic energy of the weight, which was converted to rotational energy of the paddles, which stirred the water and caused an increase in temperature of the water due to the increased internal kinetic energy of the water. The unit of energy, the joule, was named in honor of this brilliant English scientist. Measurements showed that
1 calorie = 4.19 joules (J) = 4.19 Newton-meters (N-m).
Occasionally you will run into the older, English system of units for energy in which
1 British Thermal Unit (BTU) = 778 foot-pounds (ft-lb) = 1.1 kJ.
So we can put hot materials to work for us, since heat is a form of energy and energy is an ability to do work. We most often use this idea to run the internal combustion engine in our cars. In igniting the fuel in the engine, the gases expand pushing up the piston and doing work which in the end causes the car to move.
Work done by expansion of gas = P V
if the temperature is held constant, so no heat is added or removed, where work is in joules, P is the pressure in N/m2, and volume is in m3.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is another way of stating that during any process where heat is moved from a hotter material to a cooler material (against the natural direction of heat flow), some amount of energy is degraded to heat which can no longer be used to do useful work. Entropy is a measure of the amount of wasted heat in the system. It is a measure of the amount of disorder in the system.
Entropy Change = heat added / Kelvin Temperature
The entropy changes for reversible processes are bigger than those for non-reversible (real life) processes which have friction. Another way to express this law is that over time the amount of entropy in the universe increases.
Example 1 - What appliance can actually cool a room (lower its total internal kinetic energy): a fan, a refrigerator with the door open, a refrigerator with the door closed, an air conditioner in the middle of the room or an air conditioner partially exposed to the outside?
Only the air conditioner exposed to the outside can lower the internal energy of the room, by removing heat and exhausting it to the outside. All of the other appliances consume electric energy which will add some wasted heat to the room and will increase the room's total internal energy, even if a small area of the room (like the inside the refrigerator) is made cooler. However, the air conditioner exposed to the outside is able to send that wasted heat outside the system of the room.
Example 2 - When water vapor condenses in the air how does the heat flow?
When water vapor condenses, it releases heat causing the surrounding air to become warmer.