Explain the structure of financial systems
In direct finance borrower-spenders borrow funds straight from lenders in the financial markets by selling them securities. In indirect finance a financial intermediary stands among the lender-savers and the borrower-spenders: the intermediary assists to transfer funds from one to the other. This suggests that financial markets as well as intermediaries are alternatives that perform more or less the same function but in different ways and perhaps with different degrees of success. Note but that the process of indirect finance known as financial intermediation is the most significant way of transferring funds from lenders to borrowers.
This contrasts with the attitude of the media to centre mainly on financial markets .Another significant function of a financial system is the monetary function. The introduction of money into the economy enables savers and spenders to separate the act of sale from the act of purchase and allows them to overcome the major problem of barter which is the double coincidence of wants each of the two parties involved in a transaction has to want simultaneously the good the other party is offering to exchange. The financial system provides a selection of payment mechanisms example debit cards, cheques and credit cards to enable one party to pay another.
Financial systems as well provide mechanisms for risk to be transferred. For instance insurance contracts permit a party such as a firm or household to transfer the risk of loss of wealth due to theft or else fire to another party such as an insurance company. The firm or else household will pay a fee (insurance premium) for this transfer. The insurance company by providing a large number of insurance contracts is better capable of manage the risk than an individual firm or household as they can obtain benefits of pooling and diversification. Therefore a more efficient allocation of risk results. Briefly the main functions of financial systems are to
- Offer the mechanisms by which funds are able to be transferred from units in surplus to units with a shortage of funds in order to directly or indirectly facilitate lending and borrowing (as shown in Figure 2.1)
- Make possible wealth holders to adjust the composition of their portfolios
- Offer mechanisms for risk transfer
Activity 2.1
There are lots of key terms all collected in the 'Key terms' section at the end of each section. Accumulate your own glossary with full definitions and comments on each of these terms and use it for revision.
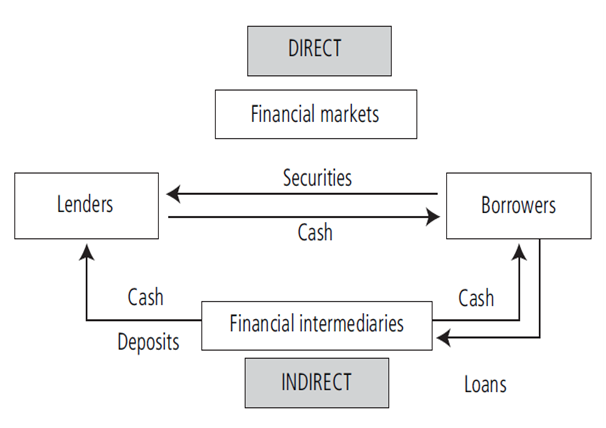
The structure of financial systems: financial markets, securities and financial intermediaries
From a structural opinion a financial system is able to be seen in terms of the entities that compose the system. A financial system comprises securities, financial markets and financial intermediaries.
Financial markets are markets in which finances are moved from people who have an excess of available funds and lack of investment opportunities to people who have investment opportunities (and lack of funds). They as well have direct effects on personal wealth, and the behaviours of businesses and consumers. Therefore they contribute to increase the production and the efficiency in the overall economy. Financial markets such as bond as well as stock markets are markets in which securities are traded.
Securities as well called financial instruments are financial claims on the issuer's future income or assets. They represent monetary liabilities for the individual or firm that sells them borrower or issuer of the financial claim in return for money and monetary assets for the buyer lender or investor in the financial claim. By definition thus the sum of financial assets in existence will exactly equal the sum of liabilities.
Governments and corporations increases funds to finance their activities by issuing debt instruments (bonds) and equity instruments (shares, known in the USA as stocks). Bonds are securities that assures to make periodic payments of a sum of money for a specified period of time. Stocks are securities that symbolize a share of ownership in the firm.
Financial intermediaries are monetary agents who specialise in the activities of buying and selling (at the same time) financial contracts (loans and deposits) and securities (bonds and stocks). Note that financial securities are effortlessly marketable while financial contracts cannot be easily sold (marketed). Banks form the main financial institution in our economy. They accept deposits or else loans by individuals or firms to banks and make loans (sums of money lent by banks to individuals or firms) therefore they borrow deposits from people who have saved and in turn make loans to others. In recent years, other financial intermediaries such as pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds and investment banks have been growing at the expense of banks.