The formation of a co-ordination compound involves reaction between a metal ion and ligands. If the force of attraction of the metal ion with ligands is strong a stable complex may result. Generally the complex ions are highly stable. Though, their possibility of dissociation in aqueous solutions cannot be lined out completely though these may be dissociated to a small degree. Thus, a chemical equilibrium may be established between the undissociated complex and the dissociated ions.
(MLn)b+ 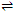 Ma+ nLx-
Ma+ nLx-
Here a+, x- and b+ are the charges on the metal atoms, ligand and complex respectively. Thus, the equilibrium constant of the above reaction is given as
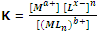
The reciprocal of the above constant K, is called stability constant (K8). Greater the value of K8 more is the stability of the complex.
The magnitude of stability constant helps us to predict that what kind of ligand with a particular metal ion yields a more stable complex. In general, higher is the value of stability constant for a complex ion greater will be its stability. For example a perusal shows that complex of Cu+2 with CN- ligand is more stable than that will ammonia.
Alternatively, 1/K values are sometimes called instability constant.
The stability of complex can also be expressed in terms of its formation constant ( 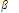 n). Let us understand this idea with the help of an example discussed below.
n). Let us understand this idea with the help of an example discussed below.
[M(H2O)n] + nL 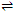 [MLn] + nH2O
[MLn] + nH2O
Follows the following steps:
Step I:
[M(H2O)n] + L 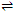 [ML(H2O)n-1] + H2O
[ML(H2O)n-1] + H2O
The formation constant for this step,
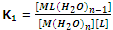
Step II:
[ML(H2O)n-1] + L ? [ML2(H2O)n-2] + H2O
The formation constant of step 2,
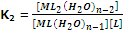
Similarly, [ML2(H2O)n-2] + L ? [MLn] + H2O
Thus, for nth step the constant,
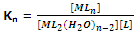
Now for the overall reaction,
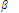 n = K1 × K2 × K3 × ..... × Kn
n = K1 × K2 × K3 × ..... × Kn
Here K1, K2, K3, .... etc are stepwise formation constants or stepwise constants while 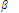 n is termed as overall formation constant or overall or cumulative stability constant.
n is termed as overall formation constant or overall or cumulative stability constant.
|
Complex ion
|
Equilibrium reaction
|
K8
|
|
[AlF6]3-
|
Al3+ 6F- 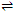 [AlF6]3- [AlF6]3-
|
6.7 × 1019
|
|
[Cd(CN)4]2-
|
Cd2+ + 4CN- 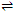 [Cd(CN)4]2- [Cd(CN)4]2-
|
7.1 × 1018
|
|
[Co(NH3)6]3+
|
Co3+ + 6NH3 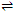 [Co(NH3)6]3+ [Co(NH3)6]3+
|
4.5 × 1033
|
|
[Cu(CN)3]2-
|
Cu+ + 3CN- 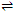 [Cu(CN3)]2- [Cu(CN3)]2-
|
2 × 1027
|
|
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
|
Cu2+ + 4NH3 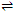 [Cu(NH3)4]2+ [Cu(NH3)4]2+
|
2.1 × 1014
|
|
[Fe(CN)6]4-
|
Fe2+ + 6CN- 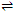 [Fe(CN)6]4- [Fe(CN)6]4-
|
1 × 1037
|
|
[Fe(CN)6]3-
|
Fe3+ + 6CN- 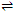 [Fe(CN)6]3- [Fe(CN)6]3-
|
1 × 1042
|
|
[PbCl3]-
|
Pb2+ + 3Cl- 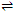 [PbCl3]- [PbCl3]-
|
2.4 × 101
|
|
[HgCl4]2-
|
Hg2+ + 4Cl- 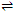 [HgCl4]2- [HgCl4]2-
|
1.2 × 1015
|
|
[Hgl4]2-
|
Hg2+ + 4I- 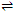 [HgI4]2- [HgI4]2-
|
1.9 × 1030
|
|
[Ni(CN)4]2-
|
Ni2+ + 4CN- 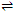 [Ni(CN)4]2- [Ni(CN)4]2-
|
1 × 1022
|
|
[Ag(NH3)2]+
|
Ag+ + 2NH3 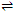 [Ag(NH3)2]+ [Ag(NH3)2]+
|
1.6 × 107
|
|
[Ag(CN)2]-
|
Ag+ + 2 CN- 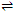 [Ag(CN)2]- [Ag(CN)2]-
|
5.6 × 1018
|
|
[Ag(S2O3)2]3-
|
Ag+ + 2S2O32- 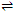 [Ag(S2O3)2]3- [Ag(S2O3)2]3-
|
1.7 × 1013
|
|
Zn(NH3)4]2+
|
Zn2+ + 4NH3 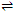 [Zn(NH3)4]2+ [Zn(NH3)4]2+
|
2.9 × 109
|
|
[Zn(CN)4]2-
|
Zn2+ + 4CN- 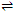 [Zn(CN)4]2- [Zn(CN)4]2-
|
1 × 1018
|
While studying the formation of complexes in solution, two kinds of stability of complexes come into question. These are:
Thermodynamic stability: it is a measure of the extent to which the complex will form or will transform into another species when the system has reached equilibrium. This kind of stability deals with metal-ligand bond energy, stability constant etc.
Kinetic stability: this refers to speed with which the transformations occur so as to attain equilibrium. From kinetic view point a complex may be inert or labile rather than stable or unstable. Complexes in which ligands are rapidly replaced by others are called labile or non inert complexes while those in which substitution occurs slowly are called inert complexes.
An example is discussed below to illustrate the above idea.
Cd2+ + NH3 [Cd(NH3)]2+ ...... K1 = 102.65
[Cd(NH3)]2+ + NH3 [Cd(NH3)2]2+ ..... K2 = 102.10
[Cd(NH3)2]2+ + NH3 [Cd(NH3)3]2+ ..... K3 = 101.44
[Cd(NH3)3]2+ + NH3 [Cd(NH3)4]2+ ...... K4 = 100.93
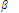 4 = K1 × K2 × K3 × K4 = 102.65 × 102.10 × 101.44 × 100.93 = 107.12
4 = K1 × K2 × K3 × K4 = 102.65 × 102.10 × 101.44 × 100.93 = 107.12