Explain the Photoelectric Effect Atomic Models
Heinrich Hertz first observed the photoelectric effect in 1887. He noticed that if a photon with enough energy is absorbed by an atom or molecule in a solid, it can cause the release of an electron moving with kinetic energy equal to the energy left over after overcoming the electron's binding energy. Einstein's interpretation of this effect in 1905 earned him the Nobel Prize in 1921.
The photoelectric effect has some interesting features. Below a threshold frequency of light, no electrons are emitted, no matter how intense the light is. Different materials have different threshold frequencies. When the frequency of the radiation is above the threshold frequency, even the weakest radiation will make electrons be emitted, and the maximum speed of the electrons is the same as you increase the intensity of the radiation. The number of electrons emitted increases with increasing intensity of the incoming radiation.
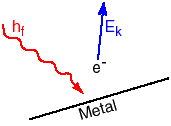
Einstein explained these features by considering radiation to be packaged as a quantum of energy determined by the frequency of the radiation, E = h f. One quantum of energy is a particle called a photon of that frequency radiation. To remove an electron, the photon must supply more energy than the work function of the material, W, the minimum amount of energy to liberate an electron from the material. The electron is emitted with kinetic energy Ek,
Ek = h f - W
where Ek and W are measured in joules, h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js, and f is in hertz. Sometimes a smaller unit of energy, the eV is used. One eV = 1.6 x 10-19 joule. If the frequency of the radiation is increased, the kinetic energy of the electron will be increased.