Explain the periodic table of the elements ?
Periodic Table of the Elements : An element is a pure substance composed of atoms all of a single kind. It cannot be broken down chemically into different forms of matter. About 92 elements occur in nature, and others, with atomic numbers 93 to 112, can be made in the laboratory. Living organisms contain only about 20 elements in more than minute quantities.
Names and properties of elements are listed in a chart called the Periodic Table of the Elements. The properties of an element can be predicted to some extent by its position in the Periodic Table.
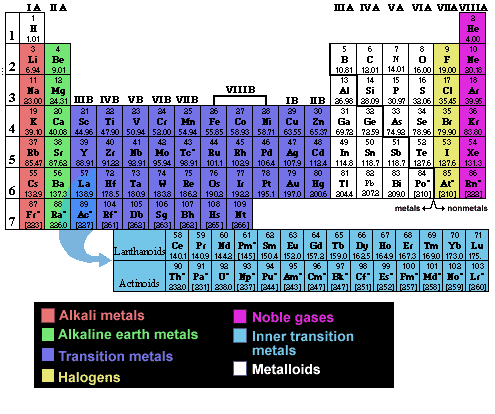
In the table, each element is represented by a symbol. The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number, and by convention the atomic number is listed at the lower left of the symbol as a subscript. The superscript to the left upper corner of the symbol is the atomic mass (mass number), or the approximate mass of the specific isotope of that element.
Isotopes are forms of an element with different atomic masses that occur because the number of neutrons in the nucleus can vary without essentially changing chemical properties of the element. In other words, isotopes behave exactly alike in terms of how they interact electrically with other elements, even though their masses differ, because neutrons are electrically neutral.
Most elements have two or more isotopes. Most hydrogen atoms are made of one proton and one electron. However, in nature, about 1 out of every 6,500 hydrogen atoms has a neutron as well as a proton in its nucleus. This isotope is called deuterium; its symbol is written 2H.