Explain the Optical Instruments?
The lenses you use most often are the ones in your eyes. The front of your eye has a convex lens whose focal length can be changed by the muscles in your eye. As the muscles contract, the lens is squeezed and becomes more curved, shortening the focal length. When you look at objects far away, the muscles in your eye relax, so that the lens becomes flatter and the focal length of the lens becomes longer.
Those of us who are near-sighted or far-sighted have lost one end of the range of muscular adjustment to the lens of our eye. The near-sighted among us can no longer relax enough to see things that are far away, so glasses or contact lenses that diverge the light before it enters your eye are used. Those who are far-sighted have trouble shortening the focal length of the lens of the eye to see things up close. Glasses or contact lenses that converge the light rays before they enter the eye will help correct the problem.
You might wonder how the eye deals with the inverted image that you always get with a single converging lens with an object at f or larger. Your brain is used to receiving all the images at the retina of your eye upside down, and it automatically inverts them so that to our brain it seems right side up.
A camera is similar to the eye except it usually has more than one simple lens, a shutter instead of an eyelid, and film at the position of the retina.
A compound microscope is two convex lenses used in combination to create an image which is greatly magnified and inverted. The eyepiece is the lens nearer the eye, and the objective is the lens toward the object. The magnification of the two lenses working together is given by
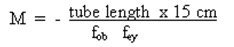
where fob is the focal length of the objective lens and fey is the focal length of the eyepiece, M is the total magnification, and all lengths are given in cm.
A simple refracting telescope also consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece. A good telescope needs light-gathering power which will determine how bright the image is. The larger the objective, the greater the light gathering power of the telescope and, unfortunately, the more expensive the telescope is. For a simple refracting telescope, the magnification, m, is given by
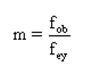
where fob is the focal length of the objective lens and fey is the focal length of the eyepiece. Another consideration is the resolving power of the telescope, meaning its ability to differentiate between two distant stars whose angular separation is small. The approximations made for thin lenses versus real lenses start catching up with us as well. Spherical aberration - rays that are not focused to exactly the focal point but a little in front or in back of the focal point - becomes important, as does chromatic aberration, in which a real lens does not focus all the wavelengths of light at the same point. Field of view must be considered as well as other design parameters.