Explain the Nuclear Notation?
Chemical reactions deal with the number of electrons exchanged or shared. Nuclear reactions, on the other hand, involve protons and neutrons and stuff from the nucleus. During nuclear reactions atoms gain and lose protons and neutrons. This is odd, considering that the number of protons in an atom defines the type of element. Nuclear chemistry often involves changing one element into another.
Radioactive elements spontaneously break up. You can also change the nuclei of these elements by hitting them with fast-moving particles. Rutherford used naturally occurring alpha particles from radioactive elements to bombard the nuclei. Particles from accelerators are now frequently used. In any nuclear reaction, atomic number and mass number are conserved. The sum of the atomic numbers on the left side of the equation must equal the sum on the right side. Also, the sum of the mass numbers on the left side must equal the sum on the right. Atomic number is written as a subscript and the mass number as a superscript of the element.
This is how nuclear chemists think about each atom:

Nuclear changes can be represented using the same reaction format you are used to.
The numbers you will be balancing in a nuclear reaction will be protons and neutrons. If is important to remember which isotope you are working with.
A typical nuclear reaction would be:
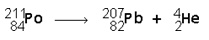
Polonium turns into lead and a helium nucleus is released.
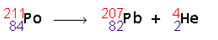
Notice that the numbers or nucleons across the top add up. The numbers on the bottom add up too! Conservation of mass is achieved.
Here's another nuclear reaction:
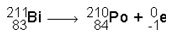
This one is kind of sneaky. Notice how the electron on the right has a negative 1 in place of the atomic number. When you add up the numbers, though, it all balances out.