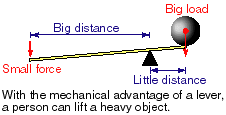
Explain the Machine
A machine is anything that makes work easier. Does it do the work for you? No, you don’t get something for nothing in this world, but it can make the work easier for you to do by multiplying your force. A machine usually lessens how much force you have to push or pull with or changes the force’s direction, but makes the distance you have to push or pull through larger. Machines let us trade off endurance (long distances) for strength (large forces). If there is no friction,
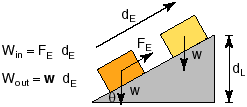
your force x your distance = the force on the load x distance the load moves
(the work you put in) = (the work done on the load).
little force x big distance = big force x little distance
With friction, there are small losses of energy along the way and work done on the load is a little less than the work you put in by the amount of work to overcome friction.
An inclined plane makes it easier to move a heavy object up by lessening the force but making you push over a longer distance than you would need to lift it. Work is force x distance, and equal in both cases (with no friction). But wouldn’t you rather push a large heavy box up a ramp than lift it to the same height?
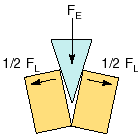
A wedge changes a downward force into a sideways force to help cut things, like when you pound a wedge into a log to split the log into two smaller pieces. A knife is a commonly used wedge, if you push down you cut the sandwich into two pieces.
A screw both lets you use less force over a longer distance and changes the direction of the force needed to fasten two pieces together. It can be looked at as an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. Which is easier to pull out of a board, a nail or a screw?
These three machines make up the inclined plane group, which includes ramps, wedges and screws.
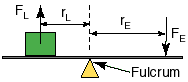
A lever is a board balanced on a point of support that can be rotated to lift something. The seesaw on a playground is an example - if you sit on one end of it, you can lift someone on the other end (the load). The point of support or where it rotates is the fulcrum. The lever can lessen the force needed (applied force)and it does change the direction of the force.
A wheel and axle makes it easier to push a car forward than if you had to slide it along the ground with no wheels. The axle must move with the wheels.
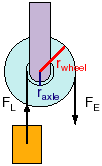
A pulley is a rope over a cylinder which changes the direction of the force: you pull the rope down and the piano moves up. More than one pulley can also lessen the force needed but you need much more rope.
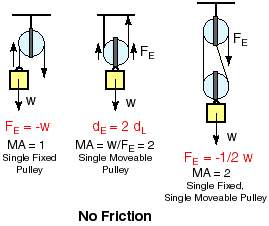
These three machines make up the lever group which includes levers, wheels and axles and pulleys.
A measure of how much a machine makes work easier is its mechanical advantage (MA).
MA = force on the load / force into machine = Fout / Fin
Efficiency measures how much of the work you put in gets to the load. If you make our assumption of no friction, the efficiency of machines would be 100% at all times. Obviously this does not happen in this world.
Efficiency = useful work output / total work output
=Workout / Workin
More Work and Energy Problems
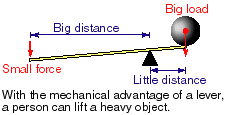
2. If you use a lever and push with a 1 Newton force to pick up a 100 Newton boulder, this lever gives you a mechanical advantage of
MA = 100 newtons /1 newton = 100
Your force of 1 Newton is being multiplied by the mechanical advantage of the lever, 100.
Did the lever do more work than you did?
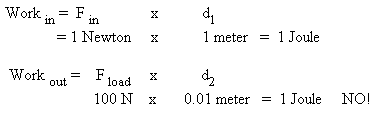
3. If you put in 200 joules of work to lift a 100 Newton box 1 meter with
a pulley system, the pulley system’s efficiency is
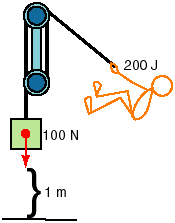
Efficiency = work out/ work in = 100 N * 1 meter / 200 joules = ½ * 100%
=50%
or half the work input is used to overcome friction, which turns that energy into heat, and only 50% is left to do useful work and lift the load.