Explain the Kidney Structure in human biology?
The body's two kidneys are located in the small of the back, one behind the stomach and one behind the liver. Each kidney is composed of a compact outer layer where urine is formed, and a hollow inner sac called the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is a branched collecting chamber that funnels waste out of the kidney. It also serves as a passageway for the renal artery, which carries blood to the kidney, and the renal vein, which carries away filtered blood.
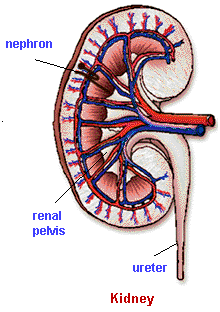
The outer layer of the kidney is divided into the renal medulla and the overlying renal cortex. Structures called nephrons are found in the cortex and extend into the medulla. The kidney contains approximately one million nephrons, which carry out the major functions of the urinary system.
An arteriole supplies each nephron with blood, and a venule drains it. The arteriole runs into a capillary bed called a glomerulus, which is enclosed in a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The glomerulus and its surrounding Bowman's capsule compose the renal corpuscle.
The renal tubule is divided into three segments. The proximal convoluted tubule, located in the cortex, leads to a tubule segment known as the loop of Henle as it extends down into the medulla, where it makes a hairpin loop before returning to the cortex. At this point it becomes the distal convoluted tubule, so called because it is away from, or distal, to the glomerulus. Several tubules join a collecting duct, which passes through the medulla adjacent to the loop of Henle.