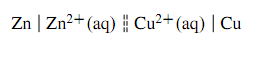Explain the Electrode reactions and the cell reaction?
A cell diagram, with its designation of the left and right electrodes, allows us to write reaction equations for the cell. These equations are written according to the convention that electrons enter at the right terminal and leave at the left terminal. At each electrode there is an electrode reaction, or half-reaction, one for reduction at the right electrode and the other for oxidation at the left electrode. The reaction equations for the electrode reactions include electrons as either a reactant (at the right terminal) or a product (at the left terminal). The cell reaction describes the overall chemical change; its reaction equation is the sum of the equations for the two electrode reactants with cancellation of the electrons.
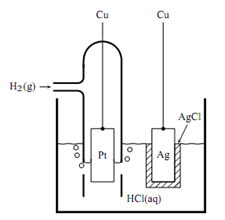
For instance, we can write the electrode reactions of the cell of Figure as follows.
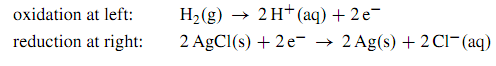
As written here, the stoichiometric numbers of the electrons have the same absolute value (2) in both reaction equations. This allows the electrons to cancel when we add the electrode reactions to form the cell reaction:
H2(g) + 2 AgCl (s) → 2H+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
The cell of Figure has a single electrolyte phase with essentially the same composition at both electrodes, and is an example of a cell without liquid junction or cell without transference. As an example of a cell with transference, consider the cell diagram
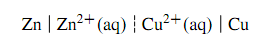
This is the zinc-copper cell depicted in Figure, sometimes called a Daniell cell. The two electrolyte phases are separated by a liquid junction represented in the cell diagram by the dashed vertical bar. If the liquid junction potential can be assumed to be negligible, the liquid junction is instead represented by a pair of dashed vertical bars: