Explain the Declaration of Multi Dimensional Arrays?
In the figure, the range in the first dimension is 3 and in the second dimension is 4. The shaded portion corresponds to the element a [2][2]. While initializing a 2D array, it is necessary to mention the second dimension (example. column) whereas the first dimension is optional.
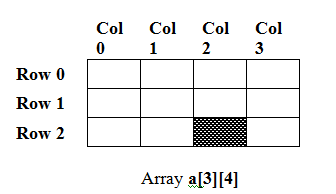
Therefore in the declarations shown below: - 'a' and 'b' are right whereas 'c' is wrong
a. static in a[3][3]={
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
b. static int a2 [][3] = {10,4,9,8,2.3} ;
c. static int a3 [][] = {10,4,9,8};]'
d. static int al [2][2] = {10,4,9,8} ;
A multidimensional array is as well possible. For illustration a 3-D array can be written as int a [3][2][2]. For identify an element of this array 3 subscripts will be needed for example a[m][n][p]. The first subscript specifies a plane number and the next two specifies the column and the row. The three-dimensional array is an array containing spatial information, which is able to be indexed by latitude, longitude and altitude.
For specifying an element of an n subscripts, n dimensional array are needed sometimes the geometric analogy breaks whenever go beyond 3-D. Still C programming language permits arbitrary number of dimension.