Explain Synchronisation and Parallel Operation
Generation, transmission and distribution of electric power have to be conducted in an efficient and reliable way at a reasonable cost with the least amount of interruptions. Consequently, in a large power system many synchronous generators are connected in parallel to a common line known as an infinite bus of fixed voltage and frequency, and pre-determined phase sequence. A number of safety requirements need to be satisfied prior to connecting a generator to the infinite bus (this is called a synchronising procedure):
(1) The operating frequency,
(2) The line voltage and
(3) The phase sequence must all be the same as those for an infinite bus.
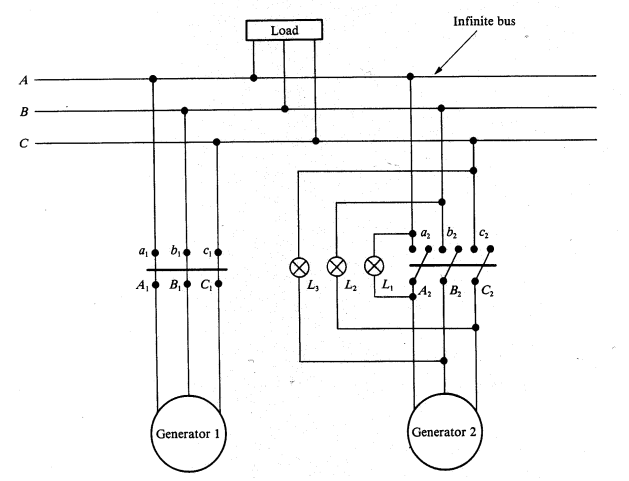
To meet an increased load demand, let us, for instance, bring a second generator into service as shown in Figure. The necessary synchronisation procedure consists of the following major steps. The speed of the incoming generator is adjusted to obtain the frequency of the induced voltage equal to that of the infinite bus. Now that the frequency match is achieved the field current can be raised to a level at which the induced voltage of the second generator is identical to the bus voltage. In order to verify the phase sequence, three lamps are connected asymmetrically as illustrated in the figure. When the phase sequence is correct, the lamp LI will be dark, while the other two lamps will glow brightly. If the phase sequence is not proper, all the lamps will glow or become dark simultaneously. When all the above conditions are met, the second generator can be safely connected to the infinite bus by closing the appropriate circuit breaker.
In addition to the lamps to check the conditions for synchronism, an electronic device (often computer controlled) called a synchroscope is also used to perform a precise switching when the above criteria are fulfilled. It provides the information on the incoming generator as to whether it is running at a lower or higher speed. At a proper speed and a correct phase sequence, the synchroscope indicates zero when the synchronising switch must be closed to connect the second generator on line. At this moment, it is neither receiving nor delivering any power. This is referred to as the floating stage of the generator. If we now increase the field current, the second generator will produce reactive power and help improve voltage regulation. Else, if an attempt is made to increase the rotor speed, the torque developed will increase and the second generator will begin to supply active power to the load.