Q. Explain Snells Law?
It is believed that Snell developed his well-known equation by purely empirical means. He made various measurements of the refracting properties of various materials and found a relationship which made accurate predictions. Later, is found that his result could be proven.
This proof of Snell's law is entirely geometric and only requires the initial assumption that the index of refraction n is related to the speed of light in the media by the following relation:
n =c/v
Where v is the speed of light in the medium, with two parallel rays approaching the interface at an angle θi from the normal. Media m1 and m2 have index of refraction ni and nr respectively.
Snell's law is typically stated as,
ni sin θi = nr sin θr,
Where i is an incident ray as well as r is a refracted ray.
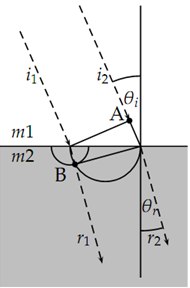
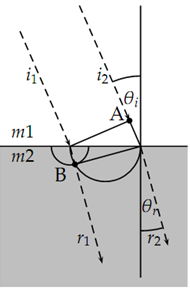
If the two rays shown travel together, then i2 just reaches point 'A' when i1 strikes the interface. i2 completes the remaining journey to the interface at velocity c/ni and covers distance x sin θi.
Fig. (19.2) shows the incident and refracted rays with critical points labelled. While i2 completes its journey to the interface, i1 is refracted into m2 travelling at the new velocity c/nr. It reaches point 'B' when i2 reaches the interface. Note that the acute angle formed by the entry point of i1 and the right triangle at 'A' is θi, and the corresponding acute angle formed by the entry point of r2 and the right triangle at 'B' is θr.
Point 'B' is found by the intersection of two circles. One is the circle centered at the entry point of i1 at the interface and with radius equal to the distance travelled in medium m2 while i2 travels its excess distance to the interface in m1. The second circle is centered halfway between the entry point of i1 and i2 along the interface, and with radius equal to half that distance x/2. This is the locus of right triangles with x as a hypotenuse.
The ratio of the two distances is the same as the ratio of the sines of angles θi/θr. But this ratio is also the ratio of the velocities of light in the respective media and is therefore inversely proportional to the indices of refraction.
Thus
ni sin θi = nr sin θr
As was to be proved.
There are other approaches to prove Snell's law but the visual appeal of a geometric proof is that the involved quantities and their relationships.