Explain New Terms for Describing Motion
As mentioned in the last chapter, the mass of a cannonball is a measure of the amount of matter (in kilograms) that would balance against it on a double pan balance. Inertia is the tendency of any object to keep moving once it starts moving and its tendency to stay at rest when it starts at rest. Mass is a measure of inertia or "laziness" that an object exhibits when you try to start it , stop it, or in any way change its motion. The more mass, the more inertia or "laziness", and if an object has less mass, it has less inertia.
To describe motion, we have to be able to say how far something has moved. So we have a standard distance called the meter. Actually, the standard meter was originally a metal bar whose length was defined to be exactly 1 meter. This bar is kept in a safe in France and used to make other bars that are the same length. These secondary standards are then sent to different areas of the world for use to make further rulers with various levels of accuracy. More recently we use atomic standards to define a meter that can be reproduced in any fairly sophisticated modern laboratory.
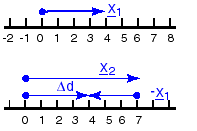
Part of describing how far a cannonball moves is describing its position. If you start at a point you choose to be "0," and a cannonball is 4 meters to the right of "0," you have defined a position vector of length 4 meters and direction to the right (+4 m), which points to the position of the cannonball.
The choice of "0" gives you the frame of reference that you will use in the problem. All positions will be measured with respect to this "0." Also, later the speed will be measured with respect to this "0" being still. If you choose your frame of reference to be the room that you are making the measurements in, and the "0" to be the zero line on the meter stick, you will be making all later measurements compared to the original position of zero on the meter stick and the speed and acceleration will be with respect to the room since we take the room as our stationary frame of reference. We could, not quite as easily, take our frame of reference for our measurements to be the center of the earth and we would then have to take into account the rotation of the room with respect to the center of the earth. But in the end the observed motion is the same with respect to the room and changing the frame of reference will not change the motion that is performed in the room.
If the cannonball moves from +4 meters to +7 meters and we treat the line along which the cannonball is moving as the x axis, its displacement vector, in moving from the first position x1 = +4 m to the second position x2 = +7 m is the change in position vector:
Δd = X2 - X1
It has a length of:
Δs = x2 - x1 = 7m - 4m = 3m
which tells you that the cannonball moved a distance of 3 meters, and is pointed to the right, so that cannonball moved towards the right, Δd = +3 m.
Next we need to be able to describe how fast the cannonball is moving. The velocity vector, is made up of the cannonball's speed and direction of motion. Speed is calculated as
Speed = Δs/ Δt
where Δs is the distance moved in meters, Δt is the time taken to move in seconds, and speed (this is an average value over Δt) is calculated in m/s. When the direction is included,
Velocity vector = v = Δd/ Δt
Where Δd is the displacement vector in meters and Δt is the time taken to move in seconds and velocity vector is in m/s.
If it took the cannonball 3 seconds to move from position 1 to position 2, its average velocity was
V= Δd/ Δt = + 3m/3s = +1m/s
Next, if the velocity vector is changing, we need to be able to describe how fast the velocity changes, how fast the cannonball is speeding up (positive acceleration) or slowing down (negative acceleration) or changing direction. The acceleration vector is:
Acceleration vector = a = Δv/ Δt = v2-v1/ Δt
where the cannonball speeds up from v1 to v2 (in m/s), in a time Δt (in seconds) and the acceleration (an average value over Δt) comes in m/s2.
If the cannonball had started at rest 2 seconds before it reached +3 m, what average acceleration did it undergo?
a = v2-v1/ Δt = +1m/s - (+0m/s) / 2s = +0.5 m/s2