Explain Lobachevskian Geometry and Riemannian Geometry ?
Nineteenth century mathematician Nicolai Lobachevsky assumed that the summit angles of a Saccheri quadrilateral are acute. Mathematicians Carl Freidrich Gauss and Johann Bolyai, who lived thousands of miles apart, also shared this belief. Based on this assumption, the new non-Euclidean geometry called Lobachevskian geometry was born. The following is a list of Lobachevskian postulates and theorems.
Postulate (Lobachevskian Postulate)
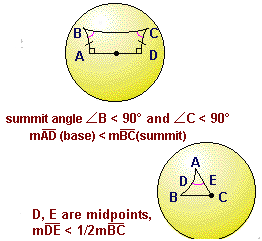
In Lobachevskian geometry, both of the summit angles of a Saccheri quadrilateral are acute.
Theorem
In Lobachevskian geometry, the base of a Saccheri quadrilateral is shorter than the summit.
Theorem
In Lobachevskian geometry, the length of the midsegment of a triangle is less than half that of the third side.
Theorem
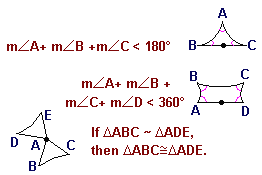
In Lobachevskian geometry, the sum of the three angles of a triangle is less than 180.
Theorem
In Lobachevskian geometry, the sum of the angles of a convex quadrilateral is less than 360.
Theorem
In Lobachevskian geometry, similar triangles must be congruent.
The Lobachevskian theorems contradict only the parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry and any conclusions based on that postulate. There is more than one parallel to a line in Lobachevskian geometry. Other than that, the Euclidean geometry is in conformity with the Lobachevskian geometry.
The conclusion of theorem 15.9 is drawn from the fact that there are no scale models in Lobachevskian geometry: if two figures have different sizes they cannot have the same shape. This is also true for Riemannian geometry in which the sum of the three angles of a triangle is more than 180.
The geometry developed by German mathematician Bernard Riemann says that there are no parallels, just like in sphere geometry. And just opposite to Lobachevskian geometry, the summit angles of a Saccheri quadrilateral are obtuse.
Postulate (Riemannian Postulate)
In Riemannian geometry, both of the summit angles
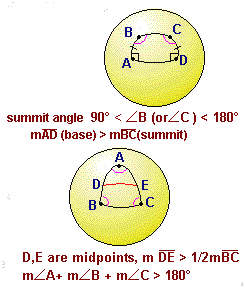
of a Saccheri quadrilateral are obtuse.
Theorem
In Riemannian geometry, the base of a Saccheri quadrilateral is longer than the summit.
Theorem
In Riemannian geometry, the length of the midsegment of a triangle is more than half that of the third side.
Theorem
In Riemannian geometry, the sum of the three angles of a triangle is more than 180.