Draw and explain the function of dual slope analogue to digital converter. Derive the equations used.
Ans.
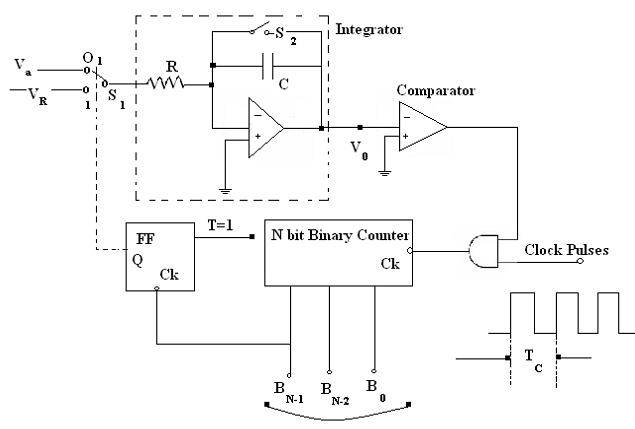
Dual slope A/D converter: This has 4 main blocks.
a. An integrator
b. A Comparator
c. A binary counter
d. A switch driver
The conversion process at T=0 along with switch S1 in position 0. It connects the analogue voltage Va to the input of the integrator. Therefore the output of the integrator will be as
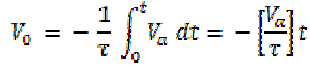
It results in high Vc. It enables the AND Gate and the clock pulse reaches the ck input of the counter, that was firstly clear. The counter counts from 00......00 to 11.....11 while 2n -1 clock pulses are applied. At the subsequent clock pulse 2n the counter is cleared and Q will be 1. It controls the state of S1 that now moves to position 1 at T1, thus connecting -VR to the input of the integrator. Here the output of the integrator starts to shift in the positive direction. The counter carries on counting until V0 is less than 0. Immediately V0 goes positive at T2, VC goes LOW disabling the AND Gate.
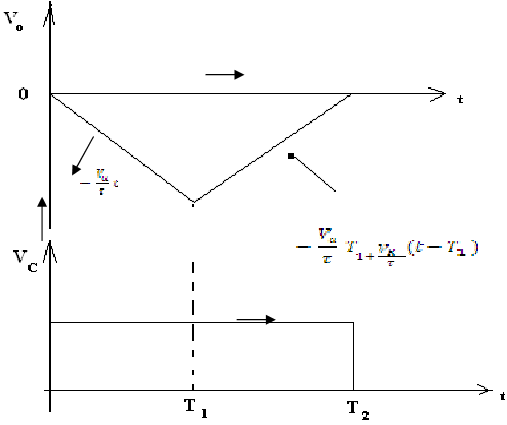
Wave form of dual slope A/D convertor
The time T1 is specified by
T1 = 2N TC, here T1 is time period of clock pulse.
Once the switch S1 is in position 1, the output voltage of the integrator is specified by
V0 = - (Va/ τ) T1 + (VR/ τ)(t - T1)
V0 = 0 at t = T2
Thus, T2 - T1 = (Va/ VR) T1 = (Va/ VR)2N TC
Assume that the count recorded in the counter be n at T2 thus T2 - T1 = n TC =(Va/ VR)2N TC
That gives n = (Va/ VR)2N