Q. Explain Digital Signal Formatting?
After quantization and coding the samples of the message, a suitable waveform has to be chosen to represent the bits. This waveformcan then be transmitted directly over the channel (if no carrier modulation is involved), or used for carriermodulation. Thewaveformselection process is known as formatting the digital sequence. Three kinds of waveforms are available:
1. Unipolar waveform, which assigns a pulse to code 1 and no pulse to code 0. The duration of a pulse is usually chosen to be equal to Tb, if binary digits occur each Tb seconds (the bit interval's duration).
2. Polar waveform, which consists of a pulse of duration Tb for a binary 1 and a negative pulse of the same magnitude and duration for a 0. This yields better system performance in noise than the unipolar format, because of the wider distinction between the two values.
3. Manchester waveform, which transmits a pulse of duration Tb/2 followed by an equal magnitude, but negative pulse of duration Tb/2 for each binary 1, and the negative of this two-pulse sequence for a binary 0. Even when a long string of 0s or 1s may occur in the digital sequence, the advantage of this format is that it never contains a dc component.
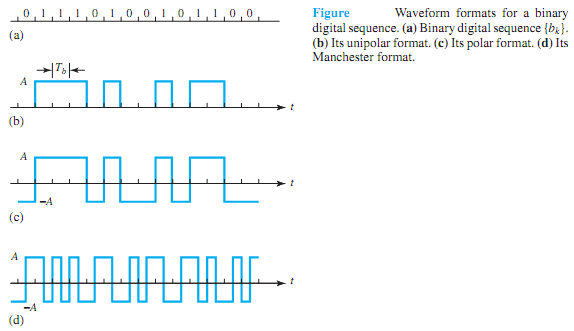
Figure illustrates these formats for a sequence of binary digits. Figure (b) shows the polar format corresponding to the coding in that case. Since it is important that a digital system not lose track of polarity while processing polar or Manchester waveforms, a technique called differential encoding is employed so as to remove the need to maintain polarity.
Because the digits in a typical digital sequence fluctuate randomly between 0s and 1s with time, the formatted waveform is then a randomly fluctuating set of pulses corresponding to the selected format.With such random waveforms, one uses the power spectral density (with units of V2 /Hz) to define the spectral content. On comparing the three waveform formats, the unipolar and polar formats both have the same bandwidth and relative side-lobe level, whereas theManchester waveform has no spectral component at direct current, but requires twice the bandwidth of the other two signals.